- Security requirements for wireless Local Area Networks - Overview
- Annex 1 - Government hot spot high-level design guidance
- Annex 2 - Wireless user to wired network connection high-level design guidance
- Annex 3 - Wired network to wired network via wireless bridge high-level design guidance
- Annex 4 - Identification of control elements from security controls
Alternate format: Annex 3 - Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge High-Level Design Guidance (ITSG-41) (PDF, 2.88 MB)
March 2013
Foreword
The ITSG-41 Annex 3 - Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge High-Level Design Guidance is an UNCLASSIFIED publication, issued under the authority of the Chief, Communications Security Establishment Canada (CSEC).
Suggestions for amendments should be forwarded through departmental communications security channels to your Client Services Representative at CSEC.
Requests for additional copies or changes in distribution should be directed to your Client Services Representative at CSEC.
For further information, please contact CSEC’s ITS Client Services area by e-mail at itsclientservices@cse-cst.gc.ca, or call 613-991-7654.
Effective Date
This publication takes effect on 2013-03-14.
Originally signed by
Toni Moffa
Deputy Chief, IT Security
Table of contents
- Foreword
- Effective Date
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- List of Abbreviations and Acronyms
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Wireless User to Wired Network Connection High-Level Design Guidance
- 3 References
- Notes
List of figures
- Figure 1 - ITSG-33 Information System Security Implementation Process
- Figure 2 - Departmental Network Zones
- Figure 3 - Departmental Network Services
- Figure 4 - Unclassified and Protected Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge
- Figure 5 - Protected C and Classified Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge
- Figure 6 - Unclassified and Protected Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge Communication Types
- Figure 7 - Protected C and Classified Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge Communication Types
- Figure 8 - Security Controls and Control Elements
List of tables
List of abbreviations and acronyms
- AES
- Advanced Encryption Standard
- CMS
- Change Management Service
- COMSEC
- Communications Security
- DAC
- Discretionary Access Control
- DHCP
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- DNS
- Domain Name Service
- EAP
- Extensible Authentication Protocol
- EAPOL
- EAP over LANs
- GC
- Government of Canada
- IDS
- Intrusion Detection System
- IEEE
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
- INE
- In-Line Network Encryptor
- IP
- Internet Protocol
- IT
- Information Technology
- ITSD
- Information Technology Security Director
- ITSG
- Information Technology Security Guidance
- LAN
- Local Area Network
- Layer 2
- OSI Model Layer 2 – Data Link Layer
- Layer 3
- OSI Model Layer 3 – Network Layer
- MCDS
- Malicious Code Defence Service
- MPLS
- Multi-Protocol Label Switching
- NAS
- Network-Attached Storage
- OSI
- Open Systems Interconnection Model
- PIN
- Personal Identification Number
- PKI
- Public Key Infrastructure
- RADIUS
- Remote Authentication Dial In User Service
- RF
- Radio Frequency
- SAN
- Storage Area Network
- SCNet
- Secure Channel Network
- SPAM
- This is not an acronym – slang name for unsolicited email
- TBS
- Treasury Board Secretariat
- TCP/IP
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
- WIDS
- Wireless Intrusion Detection System
- WLAN
- Wireless Local Area Network
1 Introduction
1.1 Purpose
The information provided in this document is intended to be used to assist in the specification of the high-level design for the secure deployment of Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) services based on the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11i (802.11) [Reference 1] Footnote 1 standard.
This document includes a reference high-level design to meet the needs of the wired network to wired network via wireless bridge business use case where employees within the physical boundaries of the department connect their wired workstations (i.e., desktops or laptops) to a wired subnet. The connectivity between the subnet and the departmental network is achieved using a WLAN bridge. Employees access the department’s end user services through the wired subnet and subsequent WLAN bridge.
The security guidance is structured to be used within the framework of Information Technology (IT) security risk management activities defined within the ITSG-33 - IT Security Risk Management: A Lifecycle Approach - Overview (ITSG-33) [Reference 2].
This document is intended for use during the high-level design activities as illustrated in Figure 1 – ITSG-33 Information System Security Implementation Process defined within the Information System Security Implementation Process (ISSIP) (refer to ITSG-33 - Annex 2 - Information System Level Risk Management Activities). The use of this document minimizes the development effort. Departments can follow its guidance to develop their own high-level designs for WLAN service deployments based on the use of reference high-level designs as a starting point. Recommendations on implementation points for technology-related control elements within the reference high-level designs are provided.
The technology-related control elements are identified from security controls selected from the ITSG-33 (Annex 3 - Security Control Catalogue). The security controls are selected to:
- Address the WLAN services deployment’s business needs for security; and
- Comply with the departmentally mandated security controls applicable to the WLAN services deployment.
Figure 1 - ITSG-33 Information System Security Implementation Process
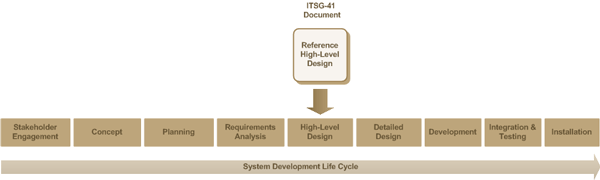
1.2 Target Audience
This document is intended for information system/security practitioners and those who are responsible for IT security risk management activities associated with the design and implementation of WLANs.
1.3 Publication Taxonomy
This document is part of a series of documents that together form the ITSG-41 publication suite. The other documents in the series are listed below:
- ITSG-41 - Security Requirements for Wireless Local Area Networks [Reference 3]
- ITSG-41 Annex 1 - Government Hot Spot High-Level Design Guidance [Reference 4]
- ITSG-41 Annex 2 - Wireless User to Wired Network Connection High-Level Design Guidance [Reference 5]
- ITSG-41 Annex 4 – Identification of Control Elements from Security Controls [Reference 6]
2 Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge High-Level Design Guidance
This section first presents the reference high-level design for a typical departmental network. The reference high-level design is then augmented with WLAN services for the wired network to wired network via wireless bridge business use case. Recommendations on where technology-related control elements may be implemented within the reference high-level designs are also provided. The process used to identify the technology-related control elements from an approved set of security controls is described in Annex 4.
2.1 Departmental Network Reference High-Level Design
The reference high-level design for the departmental network is based on the concept of zones as described in ITSG-38 - Network Security Zoning Design Considerations for Placement of Services within Zones (ITSG-38) [Reference 7].
There are four primary types of zones described within the ITSG-38. They include the public zones, public access zones, operations zones and restricted zones described in the following subsections and illustrated in Figure 2 - Departmental Network Zones (Figure 2). A department may implement multiple zones of the same type to segregate information services that exist in the same type of zone but with differing security requirements. For example, a department may use two separate public access zones; one to offer public web services to external users in the public zone that are not employees of the department; and a second to host remote access services for external users in the public zone who are employees of the department (i.e., remote access users).
Figure 2 - Departmental Network Zones
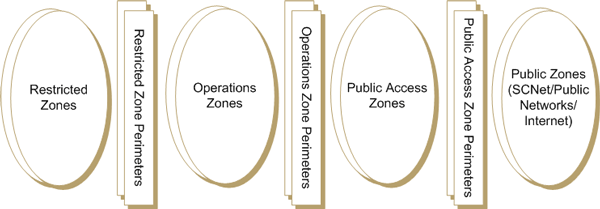
2.1.1 Public Zones
The public zones consist of communication networks that are not owned and operated by the department. These networks include the Secure Channel Network Enterprise (SCNetE) and any other public network such as the Internet. Departments normally interface directly to the SCNet which provides a Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) backbone to interconnect departments and provides a communication path to the Internet.
2.1.2 Public Access Zones
Attackers attempting to compromise a departmental network host (e.g., server) will have a greater chance of success with direct Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) connectivity to the departmental network host than if the TCP/IP communications first traverse an intermediate proxy. Since the public zones are not controlled by the department, it is therefore not desirable to allow direct TCP/IP connectivity from the public zones to departmental network hosts that support its information services. As a result, the public access zones illustrated in Figure 2 primarily host proxy and relay services that serve to mediate access between the externally accessible information services hosted by the departmental network and the public zones. Information services within the public access zones may include email proxy services, web forward proxy services, web reverse proxy services, external directory services, external Domain Name System (DNS) services and remote access services.
2.1.3 Operations Zones
The operations zones illustrated in Figure 2 primarily host the information services that are accessed by the internal users located within the physical security boundaries of the department. They also host the information services that are accessed by external users located outside the physical security boundaries of the department in the public zones. These externally accessible information services are mediated through proxy and relay services within the public access zones. Information services within the operations zones may include web and portal services, desktop services, email services, internal DNS, file share services, print services, etc. User information is processed within the operations zones but not stored. The operations zones are normally used for the processing of data rather than its storage; internal users are placed within their own operations zone. Communications between the operations zone that hosts the internal users and the operations zone that hosts the end user services are controlled through an internal user perimeter.
2.1.4 Restricted Zones
The restricted zones illustrated in Figure 2 include information management services to maintain the data processed by the information services in the operations zones and the restricted zones themselves. This data may be hosted through enterprise storage technologies such as Network-Attached Storage (NAS) or a Storage Area Network (SAN) and accessed from database servers, email servers or file servers. The restricted zones also include network and security services required to maintain the operation and security of the departmental network. The various services hosted within the restricted zones are further described below and illustrated in Figure 3 - Departmental Network Services:
- Information Management Service: The Information Management Service is responsible for the storage, safeguarding and archiving of the information created, processed and stored within the departmental network. This information can include user information (e.g., files, emails, etc.) or system information (e.g., configuration files, backup files, system images, audit records, etc.);
- Backup and Recovery Service: The Backup and Recovery Service conducts backups of user information (e.g., files, emails, etc.) and system information (e.g., configuration files, backup files, system images, audit records, etc.) within the departmental network. This information is retained and made available for recovery operations (if required);
- Networking Service (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Domain Name System (DNS), time, routing, switching, monitoring): The Networking Service is comprised of the switches, routers, firewalls and network monitoring server(s) required to establish and maintain the departmental network zoned architecture. The Networking Service also includes DHCP server(s) for assignment of Internet Protocol (IP) parameters to network hosts, DNS server(s) for name-to-IP address resolution and network time server(s) for provisioning of reference time to network hosts for system clock synchronization purposes;
- Authentication and Authorization Service: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal users, internal administrators and possibly external users and enforced within the access control functionality of departmental network services they access. The Authentication and Authorization Service includes a Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) server to support the protocols required to interface the login and access control functionality of RADIUS-enabled departmental network services, with the Authentication and Authorization Service;
- Audit Service: The Audit Service includes a central repository used to receive and store audit records generated by the departmental network’s services. The Audit Service also analyses the audit records contained in its repository and generates reports based on events of interest and notifies individuals, as necessary;
- Intrusion Detection Service (IDS) Service: The IDS Service supports near-real-time analysis of the unencrypted content of internal user, internal administrator and external user communications for unauthorized behaviour;
- Change Management Service (CMS): The CMS supports the ability to periodically audit component configurations and to compare these audited configurations against approved configurations in order to detect any unauthorized changes. The CMS also supports the ability to provision configurations to departmental network services. The CMS can report any unauthorized changes to the appropriate individual either directly (e.g., email notification) or indirectly by sending reports to the Audit Service;
- File Integrity Service (FIS): The FIS supports the functionality to detect unauthorized modifications to files within departmental network services that support the installation of a FIS agent. The FIS can report any unauthorized changes to the appropriate individual either directly (e.g., email notification) or indirectly by sending reports to the Audit Service;
- Malicious Code Defence Service (MCDS): The departmental network services are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data for malicious code and to take the appropriate action. The MCDS centrally manages malicious code protection mechanisms implemented within the departmental network services. The MCDS includes the ability to automatically update its supporting software components or signature definitions;
- Remediation Service: The Remediation Service automates the collection, analysis, and provisioning of software and software updates to the departmental network services that are compatible with the Remediation Service; and
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Service: The PKI Service supports the creation, revocation or recovery of cryptographic keys, digital identities and certificates used in information encryption/decryption operations or for cryptographic-based authentication operations.
Figure 3 - Departmental Network Services
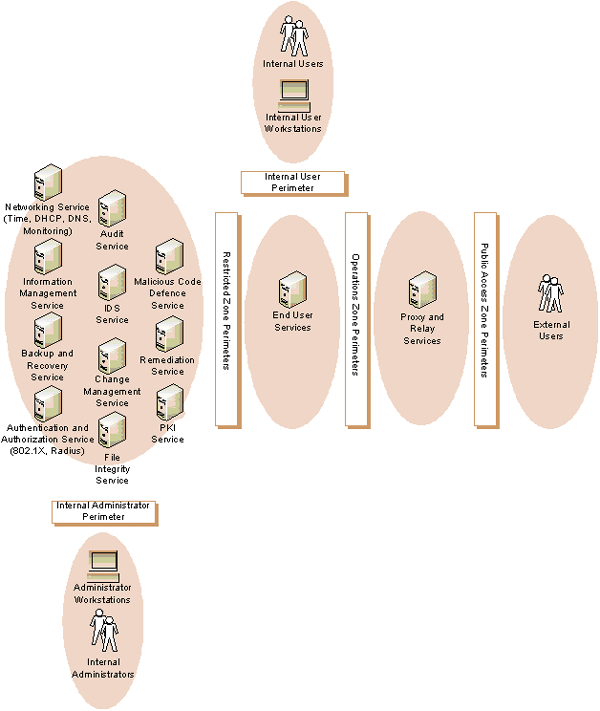
2.1.5 Management Restricted Zones
Internal administrators are placed within their own management restricted zone. Communications between the internal administrators within the management restricted zone and services within other departmental network zones are controlled through an internal administrator perimeter as well as any other perimeters traversed between the internal administrator and the service. For example, an internal administrator who is required to access a service within the public access zone would traverse the internal administrator perimeter, restricted zones and operations zones perimeters. The departmental network services should be implemented using two separate interfaces to separate management communications used for administration or maintenance (e.g., monitoring, logging, backups, software updates, etc.) from the remaining communications used to support the business activities accessed by the users.
2.2 WLAN Services Reference High-Level Design
The reference high-level design for the wired network to wired network via wireless bridge business use case differs based on the sensitivity of the information transmitted by the internal wired users over the WLAN. The differences are a result of the increase in assurance in the cryptography based products used to secure Protected C and Classified information. The ITSG-13 Cryptographic Key Ordering Manual (ITSG-13) [Reference 8] specifies that:
Only Type 1 crypto-equipment and systems that have been endorsed or approved by CSE should be used to protect electronic communications that transmit Classified and Protected C information
The commercially available 802.11 based products typically do not meet the Type 1 cryptographic standards that require successful completion of a rigorous certification process. To address the ITSG-13 requirement for Protected C or Classified data, the reference high-level design used for Unclassified, Protected A and Protected B information is augmented with additional Type 1 cryptographic components.
2.2.1 Components
The reference high-level design used for Unclassified, Protected A and Protected B wireless services information is illustrated in Figure 4 - Unclassified and Protected Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge and includes the addition of the following components to the departmental network:
- Wired Workstations: departmentally configured internal user desktops or laptops configured with an Ethernet network interface and authorized for connectivity within the internal wired user zone;
- User Wired Switch: Used to connect internal wired user workstations to the user wireless bridge;
- User And Perimeter Wireless Bridges: The user wireless bridge operates as a bridge mode access point in non-root mode to communicate with the perimeter wireless bridge that operates as a bridge mode access point in root mode;
- Perimeter Wired Switch: Used to connect the sensors and perimeter wireless bridge to the internal wired user perimeter;
- Internal Wired User Perimeter: The function of the perimeter is to control communications leaving and entering the internal wired user zone;
- Sensors: WIDS sensors can be dedicated sensors if WIDS overlay monitoring is used or implemented as part of the access points if WIDS integrated monitoring is used; and
- WIDS Service: The WIDS Service together with its sensors (overlay mode WIDS) or access points (integrated mode WIDS) support near-real-time analysis of events within the internal wired user zone and monitor for unauthorized wireless components and denial of service attacks.
Figure 4 - Unclassified and Protected Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge
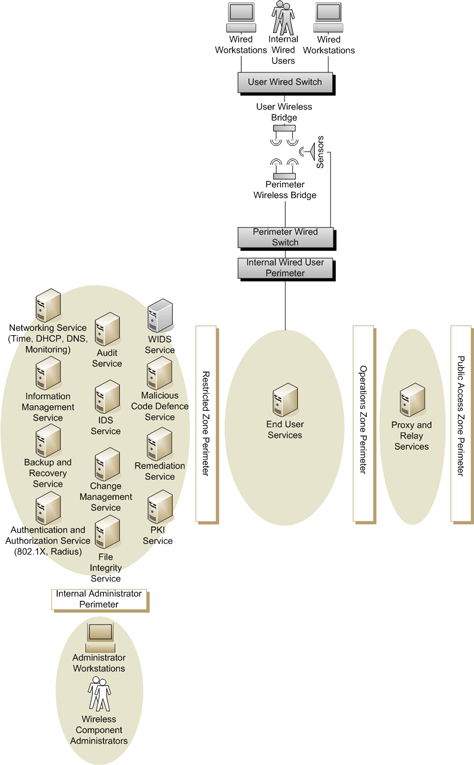
The reference high-level design used for Protected C and Classified wireless services information is illustrated in Figure 5 - Protected C and Classified Wired User Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge and includes the addition of the following components to the departmental network:
- Wired Workstations: departmentally configured internal user desktops or laptops configured with an Ethernet network interface and authorized for connectivity within the internal wired user zone;
- User Wired Switch: Used to connect internal wired user workstations to the user In-Line Network Encryptor (INE);
- User INE: Used to communicate with the perimeter INE to encrypt/decrypt internal wired user communications across the WLAN;
- User And Perimeter Black Wireless Bridges: The user black wireless bridge operates as a bridge mode access point in non-root mode to communicate with the perimeter black wireless bridge that operates as a bridge mode access point in root mode. The communications across the user and perimeter black wireless bridges are the Type 1 communications encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs;
- Black Sensors: WIDS sensors can be dedicated sensors if WIDS overlay monitoring is used or implemented as part of the access points if WIDS integrated monitoring is used;
- Perimeter Black Wired Switches: Used to connect the perimeter black wireless bridge and the black sensors to the perimeter INE and black network;
- Perimeter INE: Used to communicate with the wired workstation INEs to encrypt/decrypt internal wired user communications across the WLAN;
- Internal Wired User Perimeter: The function of the internal wired user perimeter is to control communications leaving and entering the internal wired user zone; and
- Black WIDS Service: The WIDS Service together with its sensors (overlay mode WIDS) or access points (integrated mode WIDS) support near-real-time analysis of events within the internal wired user zone and monitor for unauthorized wireless components and denial of service attacks.
INEs are used to encrypt and decrypt the communications between the user wired switch and the internal wired user perimeter. The INEs meets the Type 1 cryptographic standards required to secure Protected C and Classified communications across the WLAN. Communications, once encrypted by an INE, are Unclassified.
Since the communications between the user and perimeter INEs are Unclassified, all components that support those Unclassified communications are considered Unclassified as well (i.e., user and perimeter black wireless bridges, black sensors, perimeter black wired switch and black WIDS Service. All communications traversing the perimeter INE towards the perimeter black wired switch are encrypted. This means that the perimeter black wired switch, user and perimeter black wireless bridges, black sensors, and user wired switch are unable to communicate with the departmental network core services located behind the restricted zone perimeter, nor can they be accessed (for administrative purposes) by the wireless component administrators located behind the internal administrator perimeter.
Figure 5 - Protected C and Classified Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge
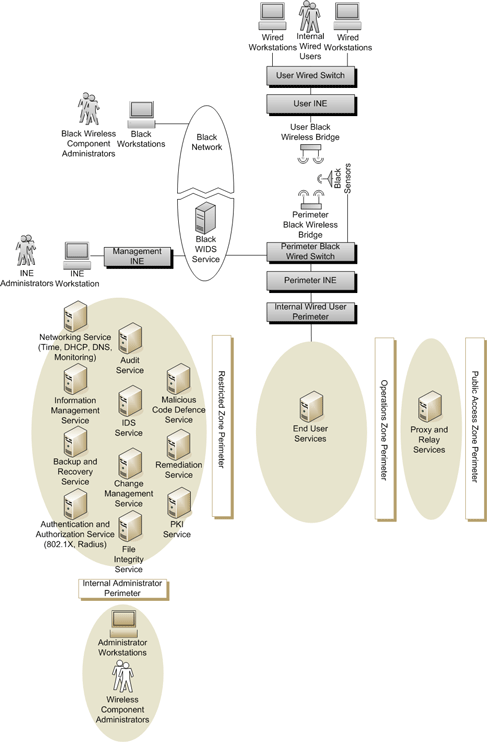
These components are instead administered from a separate black network that cannot communicate with the Protected C or Classified departmental network. The black network can be implemented solely for the purpose of administering and maintaining the operation of the perimeter black wired switch, user and perimeter black wireless bridges, black sensors, and user wired switch, or it can be a pre-existing Unclassified, Protected A or Protected B network within the department. The black network hosts the WIDS service and any core services (e.g., Authorization and Authentication Service, Audit Service, etc.) required to support the secure operation of the perimeter black wired switch, user and perimeter black wireless bridges, black sensors, and user wired switch. The perimeter INE may be remotely managed by an INE administrator using a management INE to communicate securely with the perimeter INE. The user wired switch and wired workstations are administered from the internal administrator zone provided there is network connectivity.
2.2.2 Communications
The different categories of wireless services communications for the wired network to wired network via wireless bridge business use case are illustrated in Figure 6 - Unclassified and Protected Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge Communication Types (Figure 6) and include:
- Component communications (labelled “1” in Figure 6) between the wireless components and departmental network core services discussed in Section 2.2.1 Components;
- Wireless component administrator communications (labelled “2” in Figure 6) used to administer the wireless components and that exist between the wireless component administrator workstations and the wireless components; and
- Internal wired user communications (labelled “3” in Figure 6) between the wired workstation and the departmental network’s operations zone.
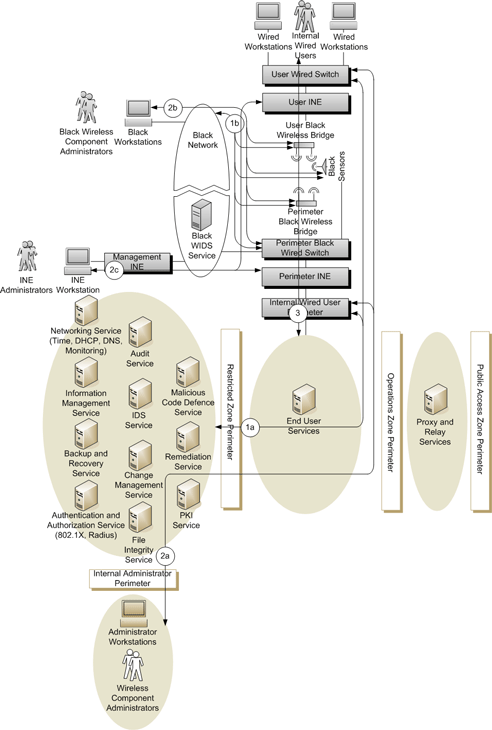
The different categories of communications for the Protected C and Classified wired network to wired network via wireless bridge business use case are illustrated Figure 7 - Protected C and Classified Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge Communication Types (Figure 7) and include:
- Component communications (labelled “1a” and “1b” in Figure 7) between the wireless components and the departmental network core services;
- Wireless component administrator communications (labelled “2a” and “2b” in Figure 7) used to administer the wireless components and that exist between the wireless component administrator workstations and the wireless components; and
- Internal wireless user communications (labelled “3” in Figure 7) between the wired workstation and the departmental network’s operations zone.
Figure 6 - Unclassified and Protected Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge Communication Types
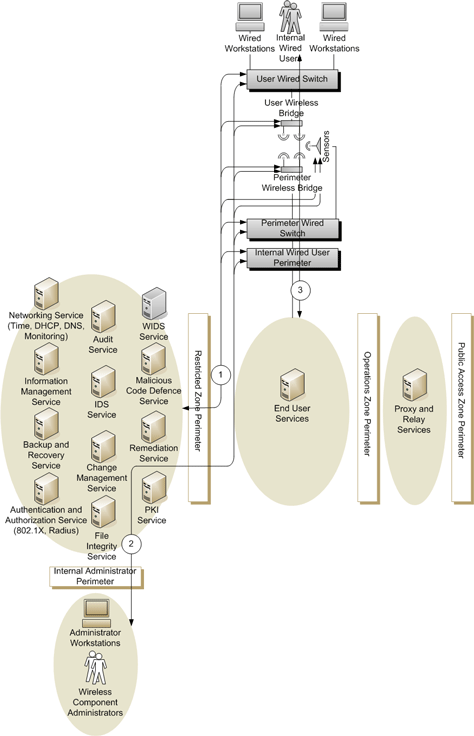
Figure 7 - Protected C and Classified Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge Communication Types
2.2.3 Concept of Operation
Wired workstations are placed within their own sub-zone within the department’s operations zone. This sub-zone is referred to as the “internal wired user zone” and is comprised of its own routable network. A sub-zone is used so that the communications between the “internal wired user zone” and the departmental operations zone can be controlled. This control is performed at the internal wired user perimeter.
Once a wired workstation has been authenticated at the device level only it has Layer 3 connectivity and is able to participate at the network layer only. The wired workstations are to be used to access end user services (e.g., desktop services, mail service, web services, etc.) within the operations zone of the departmental network. Internal wired users can only access these services once they have successfully completed a login at the user level using internal wired user account credentials configured within the Authentication and Authorization service. Once successfully logged in at the user level they can access the end user services supported by the departmental network based on the access privileges defined in the Authentication and Authorization Service and enforced by the wired workstations and other components within the departmental network.
The wireless bridges, sensors, and wired switch components and internal wired user perimeter should each support an administrative access control functionality to only allow wireless component administrators access once they have successfully completed the login process. Each component should support an accounts database used to verify the credentials of wireless component administrators during authentication. This database may be supported locally on each component, or the components may each support the ability to communicate with an accounts database supported on a separate component such as an authentication server. If all the components support the use of separate account databases then a single account can be maintained on the authentication server for all wireless component administrator logins. Otherwise a different account needs to be maintained on each component. It is assumed that the wireless component administrator accounts are maintained within a separate accounts database supported by the departmental network Authentication and Authorization Service and that the RADIUS protocol is used to support the communications between the components and the authentication server.
For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the black wireless bridges, black sensors, and perimeter black wired switch components are administered by black wireless component administrators from the black network. In addition the black wireless bridges, black sensors, and perimeter black wired switch components communicate with an authentication server supported by the black network Authentication and Authorization Service.
The internal wired user perimeter controls the communications between the wired workstations, wireless bridges, sensors, and perimeter wired switch components and departmental network core services. Communications across the internal wired user perimeter are controlled based on TCP/IP ports, source IP addresses and destination IP addresses.
2.2.4 Monitoring
The WIDS sensors monitor the 802.11 Radio Frequency (RF) medium and relay the monitored information back to the WIDS service on the wired Local Area Network (LAN) for processing. The WIDS system can be used to monitor the RF medium for attack signatures or anomalous behaviour; however, the greatest benefit is in its ability to:
- Be configured with the identification of all the authorized wireless bridges within the WLAN;
- Identify the physical location of all the authorized wireless bridges within the WLAN; and
- Detect and disable unauthorized wireless components within the WLAN coverage area.
For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the WIDS Service is supported within by a black network WIDS server and black sensors.
2.3 Technology-Related Control Element Implementation Points
Table 1 - Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge Implementation Points (Table 1) specifies all the technology-related control elements that may be considered for the wired network to wired network via wireless bridge business use case. The actual technology-related control elements used within a specific wireless services deployment are identified from the approved set of security controls using the process described in Annex 4 (illustrated in Figure 8 – Security Controls and Control Elements). Annex 4 includes examples of how the process is executed using the Protected A/Low Integrity/Low Availability and Protected B/Medium Integrity/Medium Availability security control profiles as the approved set of security controls. These profiles are defined within the ITSG-33 Annex 4.
Figure 8 - Security Controls and Control Elements
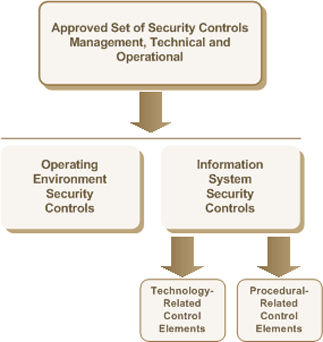
2.3.1 Technology-Related Control Element Summaries
This section provides introductory information to the recommendations presented in Table 1.
The departmental network supports internal user access to end user services using wired workstations with network connectivity through wired LANs. It is assumed that all the technology-related control elements required to secure the internal user access to end user services with network connectivity through wired LANs are implemented prior to the deployment of wireless services. This includes any technology-related control elements implemented on the wired workstations, within the end user services and within other departmental network services. The deployment of wireless services is intended to bridge two wired LAN segments. It is assumed that the same wired workstations used to access end user services with network connectivity through wired LANs are used to implement the wired workstations in the internal wired user zone. A technology-related control element that is expected to be implemented within the wired workstation configuration will be referred to in this document as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AC-2 Account Management
Account management applies to the accounts for wireless component administrator and black wireless component administrators (referred to in the remainder of this section as wireless component administrators) required to administer the wireless components (user/perimeter wireless bridges, user/perimeter wired switches, sensors, internal wired user perimeter, black user/perimeter wireless bridges, black sensors and perimeter black wired switch). Account management also applies to the internal wired user accounts used to access the end user services through the wired workstations.
The wireless components should each support an administrative access control functionality to only allow wireless component administrators access once they have successfully completed the login process. Each component should support an accounts database used to verify the credentials of wireless component administrators during authentication. This database may be supported locally on the component, or the component may support the ability to communicate with an accounts database supported on a separate component such as an authentication server. If all the components support the use of separate account databases then a single account per wireless component administrator can be maintained on the authentication server. A single account per black wireless component administrator can be maintained on an authentication server within the black network. Otherwise a different account needs to be maintained on each component.
The internal wired users authenticate to a single authentication server. This authentication is at the user level. Once successfully authenticated they are able to access the end user services in a single sign on fashion without having to re-authenticate each time a different end user service is accessed. The internal wired user accounts are maintained within a separate accounts database supported by the departmental network Authentication and Authorization Service. The Authentication and Authorization Service is also configured with each internal wired user’s privileges within the end user services. It is assumed that the wireless component administrator accounts are also maintained within an accounts database supported by the departmental network Authentication and Authorization Service.
AC-3 Access Enforcement
Access enforcement for wireless component administrators is supported by the wireless components to control what actions a wireless component administrator is authorized to perform once they are successfully authenticated.
The wireless components should each support an administrative access control functionality to control what actions the wireless component administrators can perform based on security policies defined for each component. These policies may be configured within a local policy database on each component, or the component may support the ability to communicate with a policy database supported on a separate component such as an authorization server. If the components support the use of separate policy databases then all security policies can be maintained within a single point for all wireless component administrators. Otherwise separate policies need to be configured on each component.
It is assumed that the policies defining wireless component administrator authorized actions are maintained within a separate policy database supported by the departmental network Authentication and Authorization Service and these policies are enforced within the wireless components. This Authentication and Authorization Service is implemented on the black network to support black wireless administrator access to black wireless components.
Access enforcement for internal wired users is supported by the wired workstations and end user services to control what actions a wireless component administrator is authorized to perform once they are successfully authenticated. It is assumed that the policies defining internal wired user authorized actions are maintained within a separate policy database supported by the departmental network Authentication and Authorization Service and these policies are enforced within the wired workstations and end user services. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement
The internal wired user perimeter is configured with policies that define which communications (based on TCP/IP port, source IP address, destination IP address, etc.) are authorized to enter and leave the internal wired user zone. Only authorized communications are allowed to traverse the internal wired user perimeter. All unauthorized communications are blocked. Authorized communications that traverse the internal wired user perimeter may be component-to-service, administrator-to-component, or user-to-service.
Component-to-service communications consist of communications that do not involve an internal wired user or wireless component administrator workstation. An example would be the user wireless bridge communicating with an authentication server within the departmental Authentication and Authorization Service. Administrator-to-component communications occur when a wireless component administrator logs into a wireless component for administrative purposes. User-to-service communications consist of those communications between internal wired workstations and the end user services.
AC-5 Separation of Duties
Separation of duties is related to distinct levels of access and is supported by configuring the access enforcement security policies within the Authentication and Authorization Service so that there are different groups or levels of privileges where each group or level is based on a separate role to be performed by a wireless component administrator within the wireless components. Each wireless component administrator is only assigned group(s) or level(s) of privileges for the role(s) he/she is responsible. The groups or levels of privileges are also defined in a manner that prevents a single wireless component administrator from being assigned enough privileges required to perform fraudulent activity without collusion.
Internal wired users are less privileged than wireless component administrators and are assigned privileges within the Authentication and Authorization Service to access only what they are authorized to access within the end user services. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AC-6 Least Privilege
Least privilege is enforced by configuring the access enforcement security policies within the Authentication and Authorization Service so that each internal administrator is only assigned group(s) or level(s) of privileges for the role(s) he/she is responsible.
Internal wired users are less privileged than wireless component administrators and are assigned privileges within the Authentication and Authorization Service to access only what they are authorized to access within the end user services.
AC-7 Unsuccessful Login Attempts
Account lockout is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service and enforced on the wireless components and wired workstations to help prevent unauthorized access through password guessing. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AC-8 System Use Notification
System use notification messages are displayed to wireless component administrators upon login to the wireless components and to internal wired users upon login to the wired workstations. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AC-9 Previous Logon (Access) Notification
Previous Logon (Access) Notification is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service and supported on the wireless components and wired workstations to help detect unauthorized access using the credentials for a valid account. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AC-10 Concurrent Session Control
Concurrent session limits is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and internal wired users and enforced by the wireless components and wired workstations. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AC-11 Session Lock
Session lock is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and internal wired user sessions and enforced by the wireless components and wired workstations. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AC-16 Security Attributes
Information labelling functionality is supported within the Information Management Service for any information created, processed or stored in the information system.
AC-18 Wireless Access
Internal wired user access is architected and secured using the guidance in this document.
AC-21 User Based Collaboration and Information Sharing
Access authorizations are configured in the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users. Functionality is supported on the wired workstations to determine access authorization granted to another user for collaboration and information sharing. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AU-3 Content of Audit Records
The information content that can be contained in audit records generated by the wireless components and wired workstations is dependent on the audit capability of the wireless components and wired workstations. The auditing functionality of the wireless components and wireless workstations support the ability to send audit records to the Audit Service. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AU-4 Audit Storage Capacity
The amount of storage required to maintain audit records for the components within the departmental network can be significant. The centralized logging server supported within the departmental network Audit Service would typically not have sufficient capacity for audit record storage, therefore it is assumed that the centralized logging server uses storage maintained by the Information Management Service.
If a wireless component does not support the ability to transmit its audit records to the centralized logging server, then sufficient capacity should be maintained on the wireless component itself.
AU-5 Response to Audit Processing Failures
Auditing involves each wireless component and wired workstation’s ability to generate audit records and successfully transmit them to the centralized logging server. An audit processing failure is a result of a wireless component and wired workstation’s inability to generate or store new audit records or to transmit them to the centralized logging server or for the centralized logging server to store the received audit records. This results in the loss of auditing information. The department should define a policy on the actions to take in this instance. Shutting down the information system is the most severe action as it affects availability, but in some cases may be required if a loss of auditing information cannot be tolerated. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AU-6 Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting
Audit records are not useful unless the information they contain can be analyzed in an effective manner to report on the occurrence of events of interest. Furthermore the analysis should be holistic in that it can include audit records from multiple components in a collective manner. The Audit Service supports functionality to automatically process audit records from multiple components for events of interest based upon selectable, event criteria.
AU-7 Audit Reduction and Report Generation
Since the amount of audit records can be significant (even to the point that audit records comprise the largest volume of data within the departmental network) the Audit Service reporting capability should be able to summarize the information contained in individual audit records and subsequently reduce the amount of information or number of audit records to be retained either over a long period or permanently.
AU-8 Time Stamps
In order to support the analysis of audit records to report on events of interest, a method is required to synchronize audit records from multiple components. The method used is for each wireless component or wired workstation to include a time stamp which identifies the exact time and date that each audit record was created and for the wireless components to synchronize their system clocks with each other. Time synchronization can be achieved in an automated fashion if each wireless component or wired workstation supports the ability to update its system clock based on communications with a time server supported by the Network Service using a protocol such as Network Time Protocol. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AU-9 Protection of Audit Information
The audit records may contain information that needs to be protected in terms of their confidentiality (unauthorized access), integrity (modification) or availability (deletion). Access authorizations to audit information and tools within wireless components, wired workstations and Audit Service are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service. The enforcement of these access authorizations to protect audit records should be performed at the wireless components, wired workstations as well as within the Audit Service. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AU-10 Non-Repudiation
Non-repudiation is generally applicable for business transactions or actions performed by a user. Non-repudiation functionality is supported on the wired workstations for any information created, processed or stored by the internal wired user on the workstation. Wireless component administrator actions are monitored through the auditing functionality of the wireless components and the Audit Service. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AU-12 Audit Generation
Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. The auditing functionality of the wireless components and wired workstations support reporting of audit records of authorized and unauthorized user/process events of interest to the Audit Service. The wireless components and wired workstations support the auditing of user/process events defined in AU-2 and the generation of associated audit records that can be transmitted to the central logging server (implemented within the Audit Service) for analysis and reporting. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
AU-14 Session Audit
Session audit may be required if it is believed that improper user or administrative acts are being performed. The IDS Service can be used to access the unencrypted content of wireless component administrator or internal wired user communications and log or capture the content to the Audit Service.
CM-5 Access Restrictions for Change
Access enforcement policies defined within the Authentication and Authorization Service are supported by the wireless components and wired workstations to control what actions a wireless component administrator or internal wired user is authorized to perform once they are successfully authenticated. Each wireless component and wired workstation should support the ability to audit the enforcement of access restriction and generate associated audit records that are transmitted to the central logging server maintained by the Audit Service. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
CM-6 Configuration Settings
Each wireless component or wired workstation should be configured to operate in a mode that only provides the functionality required. Any extraneous functionality or services should be disabled.
Access enforcement is supported by the wireless components or wired workstations to control what access, or modification privileges a wireless component administrator or internal wired user has with respect to the wireless component or wired workstation configuration. Authorizations for access to configuration settings are configured within the Authorization Service and enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations and wireless components. Any changes to the wireless component or wired workstation configurations should be performed through the Change Management Service and reported to the Audit Service. The File Integrity Service may be used to detect unauthorized changes to the wireless component or wired workstation configuration. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
CM-7 Least Functionality
Each wireless component and wired workstation should be configured to operate in a mode that only provides the functionality required. Any extraneous functionality or services should be disabled. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
CM-8 Information System Component Inventory
The Change Management Service retains information pertaining to the authorized configuration of the wireless components and wired workstations and periodically audits them to verify their operating configurations match their authorized configurations. The WIDS Service may be used to monitor for unauthorized components/devices connected to the internal wired user zone.
CP-9 Information System Backup
The amount of storage required to maintain system and user-level information backups for the departmental network can be significant. The Backup and Recovery Service therefore uses storage maintained by the Information Management Service to store backups of system and user-level information.
The Backup and Recovery Service periodically accesses the wireless components with administrator privileges to create backups of their system-level information. The Backup and Recovery Service periodically accesses and creates backups of the internal wired user data maintained by the Information Management Service.
CP-10 Information System Recovery and Reconstitution
The Backup and Recovery Service accesses the system-level information backups maintained by the Information Management Service for recovery purposes. The wireless components’ system-level information is used to restore a wireless component to a known state following failure or compromise.
IA-2 User Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users)
The authentication method for wireless component administrators and internal wired users will depend on the level of protection required and may include password/PINs, multifactor authentication, one time password, certificate-based authentication, or group authenticators. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
IA-3 Device Identification and Authentication
The user wireless bridge bi-directionally authenticates itself to the perimeter wireless bridge using cryptography. The authentication is supported by the 802.1X port-based authentication functionality of the Authentication and Authorization Service.
IA-4 Identifier Management
The use of dynamic management of identifiers, attributes, and associated access authorizations is not applicable to the business use case.
IA-5 Authenticator Management
The authentication method for wireless component administrators and internal wired users will depend on the level of protection required and may include password/PINs, multifactor authentication, one time password, certificate-based authentication, or group authenticators. If a password/PIN is used for wireless component administrators, the password/PIN will comply with the password complexity requirements. If the authentication method for wireless component administrators or internal wired users is certificate-based and the certificates are issued by the departmental network PKI Service, the authentication process will:
- Validate certificates by constructing a certification path to a trusted certificate authority;
- Establish user control of the corresponding private key; and
- Map the authenticated identity to the user account. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
IA-6 Authenticator Feedback
Feedback of authentication information is obscured during wireless component administrator and internal wired user logins by the authentication mechanism supported on the wireless components and wired workstations. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
IA-7 Cryptographic Module Authentication
If a cryptographic module is used within the authentication method for wireless component administrators or internal wired users, its use will meet the requirements of applicable GC guidance for authentication to a cryptographic module. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SC-2 Application Partitioning
The wireless component administrators log into and administer the wireless components whereas the internal wired users log into the wired workstations. The wireless component administrator and internal wired user functionalities are separated both in capability and method of access. The Network Service includes support for a management sub-zone to separate wireless component administrator communications from internal wired user communications.
SC-3 Security Function Isolation
The functionality accessed by internal wired users (i.e., access to end user services) is separated by the security functionality (accessed by wireless component administrators) of the wireless components. The Network Service includes support for a management sub-zone to separate wireless component administrator communications from internal wired user communications.
SC-4 Information in Shared Resources
Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators that define what information the users and administrators are authorized to access. These authorizations prevent unauthorized and unintended information transfer via shared system resources. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SC-5 Denial of Service Protection
The WIDS Service together with its sensors (overlay mode WIDS) or access points (integrated mode WIDS) monitor for denial of service attacks originating from the internal wired user zone against the departmental network or other networks while the IDS Service monitors for denial of service attacks within the rest of the departmental network.
SC-6 Resource Priority
The Network Service’s routers support the assignment of traffic volume thresholds for network traffic types to limit use of resources by priority through traffic types.
SC-7 Boundary Protection
The internal wired user perimeter is configured with policies that define which communications (based on TCP/IP port, source IP address, destination IP address, etc.) are authorized to enter and leave the internal wired user zone.
SC-8 Transmission Integrity
Encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments additional encryption of communications is performed between the user and perimeter INEs. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone.
SC-9 Transmission Confidentiality
Encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments additional encryption of communications is performed between the user and perimeter INEs. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone.
SC-10 Network Disconnect
The internal wired user perimeter can be configured to terminate network connections after a defined period of inactivity.
SC-11 Trusted Path
Wireless component administrators access the wireless components using their administrator workstations located within the management sub-zone implemented by the Network Service. The information flow policies enforced within the restricted zone, operations zone and internal wired user perimeters ensure that administration of the wireless components can only be performed from wireless component administrator workstations located in the management sub-zone. The path between the wireless component administrators and the wireless components is therefore trusted.
Authentication and authorizations to security functions are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and enforced within the login and access control functionality of the wireless components.
SC-12 Cryptographic Key Establishment and Management
Cryptographic key management for keys used by wireless component administrators or internal wired users (if PKI based authentication is used) is supported by the PKI Service.
SC-13 Use of Cryptography
Cryptographic mechanisms used by wireless component administrators or internal wired users (if PKI based authentication is used) is supported by the PKI Service.
SC-18 Mobile Code
The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data for mobile code and to take the appropriate action. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SC-20 Secure Name /Address Resolution Service (Authoritative Source)
This is supported by the DNS functionality of the Network Service.
SC-21 Secure Name /Address Resolution Service (Recursive or Caching Resolver)
This is supported by the DNS functionality of the Network Service.
SC-22 Architecture and Provisioning for Name/Address Resolution Service
This is supported by the DNS functionality of the Network Service.
SC-23 Session Authenticity
Encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments. Additional encryption of communications is performed between the user and perimeter INEs. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted from the internal wired user zone.
SC-24 Fail in Known State
The wireless components can fail to a known-state for specific types of failures.
SC-27 Operating System-Independent Applications
The use of operating-system independent applications may not be possible for any wireless component applications as the wireless components are typically selected from a single vendor to facilitate successful integration with each other. Moreover, the wireless components are typically appliance based components whose operation is supported through firmware rather than a standard operating system.
The use of operating-system independent applications may not be applicable for wired workstations as internal wired users are typically only comfortable with a single consistent user interface.
SC-28 Protection of Information at Rest
Wired workstations are configured to employ CSEC-approved cryptographyFootnote 2 to ensure the confidentiality of Protected and Classified data at rest. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SC-29 Heterogeneity
The use of heterogeneity through selection of diverse information technologies is supported within the wireless components. (Note: This may be difficult to achieve if the wireless components are selected from a single vendor to facilitate successful integration with each other).
SC-30 Virtualization Techniques
The wireless components use abstraction techniques to present information system components as other types of components. (Note: This may be difficult to achieve if the wireless components are firmware-based appliances rather than operating system-based components. Firmware-based appliances are typically less flexible than operating system-based components in their configuration and therefore it may not allow for the possibility to configure the appliances as other types of components).
SC-32 Information System Partitioning
The Network Service partitions the departmental network into different zones where the components residing in each zone are subject to the security policies of that zone. These zones include the restricted zone, operations zone, public access zone, management sub-zone, and internal wired user zone.
SC-33 Transmission Preparation Integrity
The wireless components protect the integrity of information during data aggregation, packaging, and transformation in preparation for transmission.
SC-34 Non-Modifiable Executable Programs
The wireless components load and execute their operating system and applications from hardware-enforced, read-only media.
SC-100 Source Authentication
The security mechanisms for source authentication are implemented within the wireless workstations and the end user services. For wireless workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SI-2 Flaw Remediation
The Remediation Service automates the collection, analysis, and provisioning of software and software updates to the wireless components that are compatible with the Remediation Service.
SI-3 Malicious Code Protection
The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data to detect/eradicate malicious code. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SI-4 Information System Monitoring
The WIDS Service together with its sensors (overlay mode WIDS) or access points (integrated mode WIDS) detect attacks, and provide identification of unauthorized use of the system within the internal wired user zone while the IDS Service monitors for denial of service attacks within the rest of the departmental network.
SI-6 Security Functionality Verification
The wireless components and wired workstations verify the correct operation of their own critical security functions upon start-up or periodically following start-up. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SI-7 Software and Information Integrity
The Change Management Service periodically accesses the wireless components with wireless component administrator privileges to obtain the current operating configuration and compares it with an archived copy of the approved configuration to detect any unauthorized changes. The File Integrity Service supports the functionality to detect unauthorized modifications to files on components that support the installation of a File Integrity Service agent.
SI-8 Spam Protection
The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the Mail Service SPAM protection functionality to inspect data to detect/eradicate malicious code. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SI-9 Information Input Restrictions
Access enforcement including the capability to input information for wireless component administrators and internal wired users is supported by the wireless components and wired workstations to control what actions a wireless component administrator or internal wired user is authorized to perform once they are successfully authenticated. This includes what internal wired users can access within the end user services. The policies defining authorized actions are maintained within Authentication and Authorization Service. This Authentication and Authorization Service is implemented on the black network to support black wireless administrator access to black wireless components.
For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SI-10 Information Input Validation
Access enforcement including the capability to input information for wireless component administrators and internal wired users is supported by the wireless components and wired workstations to control what actions a wireless component administrator or internal wired user is authorized to perform once they are successfully authenticated. This includes what internal wired users can access within the end user services. The policies defining authorized actions are maintained within the Authentication and Authorization Service. This Authentication and Authorization Service is implemented on the black network to support black wireless administrator access to black wireless components.
The wireless components, wired workstations and end user services check input information for accuracy, completeness, validity, and authenticity. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
SI-11 Error Handling
The wireless components and wired workstations support the auditing of events including error conditions and the storage of audit records on the component or workstation itself. The wireless components and workstations also support the transmission of audit records to a centralized logging server maintained by the Audit Service so that audit records from all components can be managed and analyzed in a collective manner. For wired workstations, this is implemented as a workstation baseline technology-related control element.
2.3.2 Technology-Related Control Elements Implementation Point Recommendations
This section provides a table of recommendations on where in the reference high-level design the technology-related control elements may be implemented. Only the technology-related control elements identified from the system security controls need to be considered for each business use case rather than all technology-related control elements identified in each table.
Table 1 recommends implementation points for the wired network to wired network via wireless bridge business use case. The tables also identify which technology-related control elements may be implemented as system-specific (S), common (C) or hybrid (H). A system-specific technology-related control element is addressed either solely by the components added to the departmental network for the deployment of wireless services or a combination of those components and safeguards or countermeasures that exist within the departmental network prior to the deployment of wireless services. A common technology-related control element is implemented by utilizing one or more safeguards or countermeasures that exist within the departmental network prior to the deployment of wireless services and which does not require any modification. A hybrid technology-related control element is implemented by utilizing one or more safeguards or countermeasures that exist within the departmental network prior to the deployment of wireless services and which require modification.
Table 1 - Wired Network to Wired Network via Wireless Bridge Implementation Points
| Security Control | Control Element | Implementation Points | Type S/C/H |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC-2 Account Management | AC-2-1 The organization employs automated mechanisms to support the management of information system accounts. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service Description: Automated mechanisms are implemented within the Authentication and Authorization Service to manage internal wired user accounts and wireless component administrator accounts. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
C |
| AC-2 Account Management | AC-2-2 The information system automatically terminates temporary and emergency accounts after [Assignment: organization-defined time period for each type of account]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service Description: Automated mechanisms are implemented within the Authentication and Authorization Service to terminate temporary or emergency accounts created for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
C |
| AC-2 Account Management | AC-2-3 The information system automatically disables inactive accounts after [Assignment: organization-defined time period]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service Description: Automated mechanisms are implemented within the Authentication and Authorization Service to disable inactive internal wired user accounts and wireless component administrator accounts. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
C |
| AC-2 Account Management | AC-2-4 The information system automatically audits account creation, modification, disabling, and termination actions and notifies, as required, appropriate individuals. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and Audit Service Description: Automated mechanisms are implemented within the Authentication and Authorization Service to report to the Audit Service, account management actions for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. The Audit Service will notify, as required, appropriate individuals. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and Audit Service for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
C |
| AC-2 Account Management | AC-2-5 The organization: (a) Requires that users log out when [Assignment: organization defined time-period of expected inactivity and/or description of when to log out]; (b) Determines normal time-of-day and duration usage for information system accounts; (c) Monitors for atypical usage of information system accounts; and (d) Reports atypical usage to designated organizational officials. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and Audit Service. Description: Automated mechanisms are implemented within the Authentication and Authorization Service to report to the Audit Service, atypical usage of internal wired users and wireless component administrator accounts based on normal time-of-day and duration usage. The Audit Service will notify, as required, appropriate individuals of atypical usage. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and Audit Service for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
C |
| AC-2 Account Management | AC-2-6 The information system dynamically manages user privileges and associated access authorizations. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Privileges and access authorizations are dynamically managed within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. The wireless component administrator privileges and access authorizations are enforced within the administrative access control functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter components. The internal wired user privileges and access authorizations are enforced within the wired workstations. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-2 Account Management | AC-2-7 The organization: (a) establishes and administers privileged user accounts in accordance with a role-based access scheme that organizes information system and network privileges into roles; and (b) tracks and monitors privileged role assignments. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Wireless component administrator accounts are organized within the Authentication and Authorization Service by roles that are based on privileges. These privileges are enforced within the access control functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. This security control requirement does not apply to internal wired users as their accounts are unprivileged. |
S |
| AC-3 Access Enforcement | AC-3-A The information system enforces approved authorizations for logical access to the system in accordance with applicable policy. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. The wireless component administrator authorizations are enforced within the access control functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The internal wired user authorizations are enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-3 Access Enforcement | AC-3-2 The information system enforces dual authorization, based on organizational policies and procedures for [Assignment: organization-defined privileged commands]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Dual authorizations for [Assignment: organization-defined privileged commands] are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. The wireless component administrator authorizations are enforced within the access control functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The internal wired user authorizations are enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-3 Access Enforcement | AC-3-3 The information system enforces [Assignment: organization-defined nondiscretionary access control policies] over [Assignment: organization-defined set of users and resources] where the policy rule set for each policy specifies: (a) Access control information (i.e., attributes) employed by the policy rule set (e.g., position, nationality, age, project, time of day); and (b) Required relationships among the access control information to permit access. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The [Assignment: organization-defined nondiscretionary access control policies] over [Assignment: organization-defined set of users and resources] are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. The wireless component administrator policies are enforced within the access control functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The internal wired user policies are enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-3 Access Enforcement | AC-3-4 The information system enforces a Discretionary Access Control (DAC) policy that: (a) Allows users to specify and control sharing by named individuals or groups of individuals, or by both; (b) Limits propagation of access rights; and (c) Includes or excludes access to the granularity of a single user. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Discretionary Access Control policies are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service and enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations (when accessing end user services), user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. Discretionary Access Control policies are configured to (a) allow users to specify and control sharing by named individuals or groups of individuals, or by both; (b) limit propagation of access rights; and (c) include or exclude access to the granularity of a single user. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-3 Access Enforcement | AC-3-5 The information system prevents access to [Assignment: organization-defined security-relevant information] except during secure, non-operable system states. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Access to [Assignment: organization-defined security-relevant information] is assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. The wireless component administrator access policies are enforced within the access control functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The internal wired user access policies are enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-3 Access Enforcement | AC-3-6 The organization encrypts or stores off-line in a secure location [Assignment: organization-defined user and/or system information]. |
Implementation Point(s): Information Management Service Description: Information specified by [Assignment: organization-defined user and/or system information] is secured by the Information Management Service using encryption. |
C |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-A The information system enforces approved authorizations for controlling the flow of information within the system and between interconnected systems in accordance with applicable policy. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter controls communications leaving and entering the internal wired user zone using both firewalling and content checking functionality in accordance with approved authorizations. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-1 The information system enforces information flow control using explicit security attributes on information, source, and destination objects as a basis for flow control decisions. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Information flow control enforcement using explicit labels on information, source applies to controlling information flow between information systems with different classifications (i.e., protected or classified levels) which is not an applicable requirement for the business use case. |
- |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-2 The information system enforces information flow control using protected processing domains (e.g., domain type-enforcement) as a basis for flow control decisions. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter controls communications leaving and entering the internal wired user zone using protected processing domains (e.g., domain type-enforcement). |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-3 The information system enforces dynamic information flow control based on policy that allows or disallows information flows based on changing conditions or operational considerations. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter enforces dynamic information flow control of communications leaving and entering the internal wired user zone. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-4 The information system prevents encrypted data from bypassing content-checking mechanisms. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter. Description: The internal wired user perimeter performs content checking and is configured to block any encrypted communications it encounters. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-5 The information system enforces [Assignment: organization-defined limitations on the embedding of data types within other data types]. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter performs content checking and is configured to block communications that do not comply with the [Assignment: organization-defined limitations on the embedding of data types within other data types]. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-6 The information system enforces information flow control on metadata. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter performs content checking and is configured to control communications leaving and entering the internal wired user zone based upon metadata. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-7 The information system enforces [Assignment: organization-defined one-way flows] using hardware mechanisms. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Enforcement of one-way flows using hardware mechanisms is normally a requirement for transferring information between information systems of different security levels which is not an applicable to the business use case. |
- |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-8 The information system enforces information flow control using [Assignment: organization-defined security policy filters] as a basis for flow control decisions. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter performs content checking and is configured to use [Assignment: organization-defined security policy filters] as a basis for flow control decisions. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-9 The information system enforces the use of human review for [Assignment: organization-defined security policy filters] when the system is not capable of making an information flow control decision. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Human reviews are not within scope of the business use case. |
- |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-10 The information system provides the capability for a privileged administrator to enable/disable [Assignment: organization-defined security policy filters]. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter performs content checking and the [Assignment: organization-defined security policy filters] implemented for content checking can be enabled and disabled by a wireless component administrator. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-11 The information system provides the capability for a privileged administrator to configure [Assignment: organization-defined security policy filters] to support different security policies. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter performs content checking and the [Assignment: organization-defined security policy filters] implemented for content checking can be configured by a wireless component administrator. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-12 The information system, when transferring information between different security domains, identifies information flows by data type specification and usage. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter identifies information flows by data type specification and usage. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-13 The information system, when transferring information between different security domains, decomposes information into policy-relevant subcomponents for submission to policy enforcement mechanisms. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter decomposes information into policy-relevant subcomponents for submission to policy enforcement mechanisms. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-14 The information system, when transferring information between different security domains, implements policy filters that constrain data structure and content to [Assignment: organization-defined information security policy requirements]. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter implements policy filters that constrain data structure and content to [Assignment: organization-defined information security policy requirements]. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-15 The information system, when transferring information between different security domains, detects unsanctioned information and prohibits the transfer of such information in accordance with the security policy. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter detects unsanctioned information and prohibits the transfer of such information in accordance with the security policy. |
S |
| AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement | AC-4-17 The information system: (a) Uniquely identifies and authenticates source and destination domains for information transfer; (b) Binds security attributes to information to facilitate information flow policy enforcement; and (c) Tracks problems associated with the security attribute binding and information transfer. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter (a) uniquely identifies and authenticates source and destination domains for information transfer; (b) binds security attributes to information to facilitate information flow policy enforcement; and (c) logs problems associated with the security attribute binding and information transfer. |
S |
| AC-5 Separation of Duties | AC-5-C The organization implements separation of duties through assigned information system access authorizations. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service to enforce separation of duties for internal wired users and wireless component administrators. The wireless component administrator policies are enforced within the access control functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The internal wired user policies are enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-6 Least Privilege | AC-6-4 The information system provides separate processing domains to enable finer-grained allocation of user privileges. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter keeps the wired workstations in their own network subnet to establish a separate processing domain. |
S |
| AC-7 Unsuccessful Login Attempts | AC-7-A The information system enforces a limit of [Assignment: organization-defined number] consecutive invalid access attempts by a user during a [Assignment: organization-defined time period]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: A consecutive invalid access attempts limit of [Assignment: organization-defined number] is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-7 Unsuccessful Login Attempts | AC-7-B The information system automatically [Selection: locks the account/node for an [Assignment: organization-defined time period]; locks the account/node until released by an administrator; delays next login prompt according to [Assignment: organization-defined delay algorithm]] when the maximum number of unsuccessful attempts is exceeded. The control applies regardless of whether the login occurs via a local or network connection. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Account lockout is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The account lockout functionality automatically [Selection: locks the account/node for an [Assignment: organization-defined time period]; locks the account/node until released by an administrator; delays next login prompt according to [Assignment: organization-defined delay algorithm]] when the maximum number of unsuccessful attempts is exceeded. The control applies regardless of whether the login occurs via a local or network connection. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-7 Unsuccessful Login Attempts | AC-7-1 The information system automatically locks the account/node until released by an administrator when the maximum number of unsuccessful attempts is exceeded. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Account lockout is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The account lockout functionality account/node until released by an administrator when the maximum number of unsuccessful attempts is exceeded. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-7 Unsuccessful Login Attempts | AC-7-2 The information system provides additional protection for mobile devices accessed via login by purging information from the device after [Assignment: organization-defined number] consecutive, unsuccessful login attempts to the device. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Any use of mobile devices attached to the wired workstations for information storage (i.e., USB memory sticks, external hard disk drives, etc.) which require login prior to information access, purge information from the device after [Assignment: organization-defined number] consecutive, unsuccessful login attempts to the device. |
S |
| AC-8 System Use Notification | AC-8-A The information system displays an approved system use notification message or banner before granting access to the system that provides privacy and security notices in accordance with the TBS Policy on the Use of Electronic Networks. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Login banners are configured on the wired workstations and viewed by internal wired users. Login banners are configured on the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter and viewed by wireless component administrators. Login banners are configured on the black wired/wireless components for black wireless component administrator logins. Login banners display an approved system use notification message. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-8 System Use Notification | AC-8-B The information system retains the notification message or banner on the screen until users take explicit actions to log on to or further access the information system. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Login banners are configured on the wired workstations and viewed by internal wired users. Login banners are configured on the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter and viewed by wireless component administrators. Login banners are configured on the black wired/wireless components for black wireless component administrator logins. The notification message or banner remains visible until users take explicit actions to log on to or further access the information system. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-8 System Use Notification | AC-8-C The information system, for publicly accessible systems: (a) displays the system use information when appropriate, before granting further access; (b) displays references, if any, to monitoring, recording, or auditing that are consistent with privacy accommodations for such systems that generally prohibit those activities; and (c) includes in the notice given to public users of the information system, a description of the authorized uses of the system. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: The use of publicly accessible systems is not applicable to the business use case. |
- |
| AC-9 Previous Logon (Access) Notification | AC-9-A The information system notifies the user, upon successful logon (access), of the date and time of the last logon (access). |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Date and time of the last logon notification is supported within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and provided to the user within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-9 Previous Logon (Access) Notification | AC-9-1 The information system notifies the user, upon successful logon/access, of the number of unsuccessful logon/access attempts since the last successful logon/access. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Unsuccessful login notification is supported within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and provided to the user within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-9 Previous Logon (Access) Notification | AC-9-2 The information system notifies the user of the number of [Selection: successful logins/accesses; unsuccessful login/access attempts; both] during [Assignment: organization-defined time period]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The number of [Selection: successful logins/accesses; unsuccessful login/access attempts; both] during [Assignment: organization-defined time period] is maintained within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and provided to the user within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-9 Previous Logon (Access) Notification | AC-9-3 The information system notifies the user of [Assignment: organization-defined set of security- related changes to the user’s account] during [Assignment: organization-defined time period]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Notification of [Assignment: organization-defined set of security- related changes to the user’s account] during [Assignment: organization-defined time period] is supported within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and provided to the user within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-10 Concurrent Session Control | AC-10-A The information system limits the number of concurrent sessions for each system account to [Assignment: organization-defined number]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Number of concurrent sessions limit is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-11 Session Lock | AC-11-A The information system prevents further access to the system by initiating a session lock after [Assignment: organization-defined time period] of inactivity or upon receiving a request from a user. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Session lock is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. |
S |
| AC-11 Session Lock | AC-11-B The information system retains the session lock until the user re-establishes access using established identification and authentication procedures. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Session lock is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components, for black wireless component administrator accounts. Session lock is released following successful re-login. |
S |
| AC-11 Session Lock | AC-11-1 The information system session lock mechanism, when activated on a device with a display screen, places a publically viewable pattern onto the associated display, hiding what was previously visible on the screen. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Workstation screen-lock functionality is configured and enforced by the wired workstations to display (when activated) a publically viewable pattern onto the associated display, hiding what was previously visible on the screen. |
S |
| AC-16 Security Attributes | AC-16-A The information system supports and maintains the binding of [Assignment: organization-defined security attributes] to information in storage, in process, and in transmission. |
Implementation Point(s): Information Management Service Description: Information labelling functionality is supported within the Information Management Service for any information created, processed or stored in the information system. |
C |
| AC-16 Security Attributes | AC-16-1 The information system dynamically reconfigures security attributes in accordance with an identified security policy as information is created and combined. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and Information Management Service Description: Security attributes for information that is created and combined and maintained by the Information Management Service are dynamically reconfigured by the Authentication and Authorization Service. |
C |
| AC-16 Security Attributes | AC-16-2 The information system allows authorized entities to change security attributes. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and Information Management Service Description: Security attributes assigned through the Authentication and Authorization Service for information maintained within the Information Management Service can be modified by authorized users. |
C |
| AC-16 Security Attributes | AC-16-3 The information system maintains the binding of security attributes to information with sufficient assurance that the information--attribute association can be used as the basis for automated policy actions. |
Implementation Point(s): Information Management Service Description: Information labelling functionality is supported within the Information Management Service for any information created, processed or stored in the information system. |
C |
| AC-16 Security Attributes | AC-16-4 The information system allows authorized users to associate security attributes with information. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and Information Management Service Description: Authorized internal wired users and wireless component administrators can associate security attributes assigned through the Authentication and Authorization Service to information maintained within the Information Management Service. |
C |
| AC-16 Security Attributes | AC-16-5 The information system displays security attributes in human-readable form on each object output from the system to system output devices to identify [Assignment: organization-identified set of special dissemination, handling, or distribution instructions] using [Assignment: organization- identified human readable, standard naming conventions]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and Information Management Service Description: Security attributes assigned through the Authentication and Authorization Service to information maintained within the Information Management Service is displayed in human-readable form on each object output from the system to system output devices to identify [Assignment: organization-identified set of special dissemination, handling, or distribution instructions] using [Assignment: organization- identified human readable, standard naming conventions]. |
C |
| AC-18 Wireless Access | AC-18-B The organization monitors for unauthorized wireless access to the information system. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service and sensors. Description: The WIDS service together with its sensors monitors for and report unauthorized wireless components. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| AC-18 Wireless Access | AC-18-C The organization authorizes wireless access to the information system prior to connection. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges Description: The user wireless bridge bi-directionally authenticates itself to the perimeter wireless bridge using cryptography. The authentication is supported by the 802.1X port-based authentication functionality of the Authentication and Authorization Service. |
S |
| AC-18 Wireless Access | AC-18-D The organization enforces requirements for wireless connections to the information system. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges Description: The user wireless bridge bi-directionally authenticates itself to the perimeter wireless bridge using cryptography. The authentication is supported by the 802.1X port-based authentication functionality of the Authentication and Authorization Service. |
S |
| AC-18 Wireless Access | AC-18-1 The information system protects wireless access to the system using authentication and encryption. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges Description: The user wireless bridge bi-directionally authenticates itself to the perimeter wireless bridge using cryptography. The authentication is supported by the 802.1X port-based authentication functionality of the Authentication and Authorization Service. |
S |
| AC-18 Wireless Access | AC-18-2 The organization monitors for unauthorized wireless connections to the information system, including scanning for unauthorized wireless access points [Assignment: organization-defined frequency], and takes appropriate action if an unauthorized connection is discovered. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service and sensors. Description: The WIDS service together with its sensors monitor for and report unauthorized wireless components including scanning for unauthorized wireless access points [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| AC-18 Wireless Access | AC-18-4 The organization does not allow users to independently configure wireless networking capabilities. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and wired workstations. Description: Privileges and access authorizations are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and enforced within the wired workstations. These privileges and access authorizations do not allow for internal wired users to configure wireless networking capabilities on their wired workstations. |
S |
| AC-18 Wireless Access | AC-18-5 The organization confines wireless communications to organization-controlled boundaries. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The internal wired user zone RF medium is confined to organization-controlled boundaries. |
S |
| AC-19 Access Control for Mobile Devices | NA | This security control and its technology-related control elements are not applicable to this business use case since it involves the use of wired workstations are utilized as opposed to mobile devices. | - |
| AC-21 User-Based Collaboration and Information Sharing | AC-21-B The organization employs [Assignment: list of organization-defined information sharing circumstances and automated mechanisms or manual processes required] to assist users in making information sharing/collaboration decisions. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and Information Management Service Description: The [Assignment: list of organization-defined information sharing circumstances and automated mechanisms or manual processes required] are implemented to assist users in making information sharing/collaboration decisions using information maintained within the Information Management Service with security attributes assigned by the Authentication and Authorization Service. |
C |
| AC-21 User-Based Collaboration and Information Sharing | AC-21-1 The information system employs automated mechanisms to enable authorized users to make information-sharing decisions based on access authorizations of sharing partners and access restrictions on information to be shared. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Information-sharing with non-organizational partners is not applicable to the business use case. |
- |
| AU-3 Content of Audit Records | AU-3-A The information system produces audit records that contain sufficient information to, at a minimum, establish what type of event occurred, when (date and time) the event occurred, where the event occurred, the source of the event, the outcome (success or failure) of the event, and the identity of any user/subject associated with the event. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports reporting to the Audit Service of records that contain sufficient information to establish: what type of event occurred, when (date and time) the event occurred, where the event occurred, the source of the event, the outcome (success or failure) of the event, and the identity of any user/subject associated with the event. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-3 Content of Audit Records | AU-3-1 The information system includes [Assignment: organization-defined additional, more detailed information] in the audit records for audit events identified by type, location, or subject. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports the ability to configure [Assignment: organization-defined additional, more detailed information] for events reported to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-3 Content of Audit Records | AU-3-2 The organization centrally manages the content of audit records generated by [Assignment: organization-defined information system components]. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports ability to send audit records to the Audit Service. The Audit Service maintains a central repository for all audit records. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-4 Audit Storage Capacity | AU-4-A The organization allocates audit record storage capacity and configures auditing to reduce the likelihood of such capacity being exceeded. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service and Information Management Service. Description: The Audit Service is allocated record storage capacity maintained by the Information Management Service. Auditing is configured to reduce the likelihood of exceeding the record storage capacity. |
C |
| AU-5 Response to Audit Processing Failures | AU-5-A The information system alerts designated organizational officials in the event of an audit processing failure. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service Description: The Audit Service alerts appropriate organizational officials in the event of an audit processing failure. |
C |
| AU-5 Response to Audit Processing Failures | AU-5-B The information system takes the following additional actions: [Assignment: organization-defined actions to be taken (e.g., shut down information system, overwrite oldest audit records, stop generating audit records)]. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter support the ability to perform [Assignment: organization-defined actions to be taken (e.g., shut down information system, overwrite oldest audit records, stop generating audit records)] in the event of an audit processing failure within the component. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-5 Response to Audit Processing Failures | AU-5-1 The information system provides a warning when allocated audit record storage volume reaches [Assignment: organization-defined percentage] of maximum audit record storage capacity. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service and Information Management Service. Description: The Audit Service provides a warning when allocated audit record storage volume within the Information Management Service reaches [Assignment: organization-defined percentage] of maximum audit record storage capacity. |
C |
| AU-5 Response to Audit Processing Failures | AU-5-2 The information system provides a real-time alert when the following audit failure events occur: [Assignment: organization-defined audit failure events requiring real-time alerts]. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service Description: The Audit Service provides a real-time alert when the [Assignment: organization-defined audit failure events requiring real-time alert] audit failure events occur. |
C |
| AU-5 Response to Audit Processing Failures | AU-5-3 The information system enforces configurable traffic volume thresholds representing auditing capacity for network traffic and [Selection: rejects or delays] network traffic above those thresholds. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service’s routers support the assignment of traffic volume thresholds representing auditing capacity for network traffic and [Selection: rejects or delays] network traffic above those thresholds. |
C |
| AU-5 Response to Audit Processing Failures | AU-5-4 The information system invokes a system shutdown in the event of an audit failure, unless an alternative audit capability exists. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports the ability to shutdown the component if an audit failure occurs, unless an alternative audit capability exists. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-6 Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting | AU-6-3 The organization analyzes and correlates audit records across different repositories to gain organization-wide situational awareness. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components support the ability to transmit audit records to the Audit Service. The Audit Service maintains a central repository and management point for all audit records to gain organization-wide situational awareness. |
S |
| AU-6 Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting | AU-6-4 The information system centralizes the review and analysis of audit records from multiple components within the system. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports ability to send audit records to the Audit Service. The Audit Service includes a central repository for all audit records. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-6 Audit Review, Analysis, and Reporting | AU-6-5 The organization integrates analysis of audit records with analysis of vulnerability scanning information, performance data, and network monitoring information to further enhance the ability to identify inappropriate or unusual activity. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports ability to send audit records to the Audit Service. The Audit Service includes a central repository for all audit records. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-7 Audit Reduction and Report Generation | AU-7-A The information system provides an audit reduction and report generation capability. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service Description: The Audit Service supports an audit reduction and report generation capability. |
C |
| AU-7 Audit Reduction and Report Generation | AU-7-1 The information system provides the capability to automatically process audit records for events of interest based on selectable event criteria. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service Description: The Audit Service supports functionality to automatically process audit records for events of interest based upon selectable, event criteria. |
C |
| AU-8 Time Stamps | AU-8-A The information system uses internal system clocks to generate time stamps for audit records. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service, Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports ability to generate time stamps for audit records sent to the Audit Service. Each component also supports the ability to synchronize their component clocks with a centralized Time server functionality supported by the Network Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service, Network Service and audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-8 Time Stamps | AU-8-1 The information system synchronizes internal information system clocks [Assignment: organization-defined frequency] with [Assignment: organization-defined authoritative time source]. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter support the ability to synchronize their component clocks with a centralized Time server functionality supported by the Network Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service, Network Service and the system time functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-9 Protection of Audit Information | AU-9-A The information system protects audit information and audit tools from unauthorized access, modification, and deletion. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Access authorizations to audit information and tools within wireless components, wired workstations and Audit Service are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service and enforced by the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authorization Service and Audit Service and the access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-9 Protection of Audit Information | AU-9-1 The information system produces audit records on hardware-enforced, write-once media. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service Description: The Audit Service supports the ability to produce audit records on hardware-enforced, write-once media. |
C |
| AU-9 Protection of Audit Information | AU-9-2 The information system backs up audit records [Assignment: organization-defined frequency] onto a different system or media than the system being audited. |
Implementation Point(s): Backup and Recovery Service and Audit Service. Description: The Backup and Recovery Service backs up audit records produced by the Audit Service, [Assignment: organization-defined frequency] onto a different system or media than the system being audited. |
C |
| AU-9 Protection of Audit Information | AU-9-3 The information system uses cryptographic mechanisms to protect the integrity of audit information and audit tools. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service and Information Management Service. Description: The Audit Service uses cryptographic mechanisms to protect the integrity of audit information stored and maintained by the Information Management Service. |
C |
| AU-9 Protection of Audit Information | AU-9-4 The organization: (a) Authorizes access to management of audit functionality to only a limited subset of privileged users; and (b) Protects the audit records of non-local accesses to privileged accounts and the execution of privileged functions. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service, Information Management Service user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Access authorizations to audit information stored by the Audit Service, within the Information Management Service, and audit functionality within the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service to ensure that access to management of audit functionality to only a limited subset of privileged users; and (b) protects the audit records of non-local accesses to privileged accounts and the execution of privileged functions. |
C |
| AU-10 Non-Repudiation | AU-10-A The information system protects against an individual falsely denying having performed a particular action. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports the ability to send records to the Audit Service identifying user actions. For black wired/wireless components, the security control requirement is implemented within the black network Audit Service and the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-10 Non-Repudiation | AU-10-1 The information system associates the identity of the information producer with the information. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Non-repudiation functionality is supported on the wired workstations for any information created, processed or stored by the internal wired user on the wireless workstation. |
S |
| AU-10 Non-Repudiation | AU-10-2 The information system validates the binding of the information producer’s identity to the information. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Non-repudiation functionality is supported on the wired workstations for any information created, processed or stored by the internal wired user on the wireless workstation. |
S |
| AU-10 Non-Repudiation | AU-10-3 The information system maintains reviewer/releaser identity and credentials within the established chain of custody for all information reviewed or released. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Non-repudiation functionality is supported on the wired workstations for any information created, processed or stored by the internal wired user on the wireless workstation. |
S |
| AU-10 Non-Repudiation | AU-10-4 The information system validates the binding of the reviewer’s identity to the information at the transfer/release point prior to release/transfer from one security domain to another security domain. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Non-repudiation functionality is supported on the wired workstations for any information created, processed or stored by the internal wired user on the wireless workstation. |
S |
| AU-10 Non-Repudiation | AU-10-5 The organization employs cryptography compliant with the requirements of control SC-13 to implement digital signatures. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Non-repudiation functionality supported on the wired workstations employs cryptography compliant with the requirements of control SC-13 to implement digital signatures. |
S |
| AU-12 Audit Generation | AU-12-A The information system provides audit record generation capability for the list of auditable events defined in AU-2 at [Assignment: organization-defined information system components]. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter support reporting of audit records of auditable events defined in AU-2 at [Assignment: organization-defined information system components] to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-12 Audit Generation | AU-12-B The information system allows designated organizational personnel to select which auditable events are to be audited by specific components of the system. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter is configurable by the wireless component administrators in terms of the events to be audited and reported to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-12 Audit Generation | AU-12-C The information system generates audit records for the list of audited events defined in AU-2 with the content as defined in AU-3. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter support reporting of audit records of auditable events defined in AU-2 with the content as defined in AU-3. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-12 Audit Generation | AU-12-1 The information system compiles audit records from [Assignment: organization-defined information system components] into a system-wide (logical or physical) audit trail that is time- correlated to within [Assignment: organization-defined level of tolerance for relationship between time stamps of individual records in the audit trail]. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, Network Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter support the ability to send audit records to the Audit Service. Each component synchronizes its system clock with the Time server functionality of the Network Service to ensure the audit records are time correlated within an [Assignment: Organization-defined level of tolerance for relationship between time stamps of individual records in the audit trail]. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service, Network Service and the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-12 Audit Generation | AU-12-2 The information system produces a system-wide (logical or physical) audit trail composed of audit records in a standardized format. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter support the ability to send audit records to the Audit Service. The audit records produced by the external user and external administrator gateway and proxy components are in a standardized format or converted to this format by the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| AU-14 Session Audit | AU-14-A The information system provides the capability to capture/record and log all content related to a user session. |
Implementation Point(s): IDS Service Description: The IDS Service can be used to access the unencrypted content at the internal wired user perimeter and log or capture the content to the Audit Service. |
C |
| AU-14 Session Audit | AU-14-B The information system provides the capability to remotely view/hear all content related to an established user session in real time. |
Implementation Point(s): IDS Service and Audit Service. Description: The IDS Service can be used to access the unencrypted content at the internal wired user perimeter and remotely view/hear all the content of a user session in real time. |
C |
| AU-14 Session Audit | AU-14-1 The information system initiates session audits at system start-up. |
Implementation Point(s): IDS Service and Audit Service. Description: The IDS Service can be used to access the unencrypted content at the internal wired user perimeter and log or capture the content to the Audit Service. The IDS Service has the ability to initiate the audit processes at system start-up. |
C |
| CM-5 Access Restrictions for Change | CM-5-A The organization defines documents, approves, and enforces physical and logical access restrictions associated with changes to the information system. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators which define logical access restrictions associated with changes to the information system. These authorizations are enforced within the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service, and the access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| CM-5 Access Restrictions for Change | CM-5-1 The organization employs automated mechanisms to enforce access restrictions and support auditing of the enforcement actions. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. Auditing of the enforcement of these authorizations is also enforced by the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service and the audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| CM-5 Access Restrictions for Change | CM-5-3 The information system prevents the installation of [Assignment: organization-defined critical software programs] that are not signed with a certificate that is recognized and approved by the organization. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: The wired workstations are configured such that their operating system prevents the installation of [Assignment: organization-defined critical software programs] that are not signed with a organizationally recognized and approved certificate. |
S |
| CM-5 Access Restrictions for Change | CM-5-6 The organization limits privileges to change software resident within software libraries (including privileged programs). |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators which define logical access restrictions associated with changes to software resident within software libraries (including privileged programs). These authorizations are enforced within the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service, and the access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| CM-5 Access Restrictions for Change | CM-5-7 The information system automatically implements [Assignment: organization-defined safeguards and countermeasures] if security functions (or mechanisms) are changed inappropriately. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators which define logical access restrictions associated with changes to the information system. These authorizations are enforced within the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service, and the access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. The information system automatically implements [Assignment: organization-defined safeguards and countermeasures] if security functions (or mechanisms) are changed inappropriately. |
S |
| CM-6 Configuration Settings | CM-6-B The organization implements the configuration settings. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter components are configured with the most restrictive mode mandatory configuration settings. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| CM-6 Configuration Settings | CM-6-1 The organization employs automated mechanisms to centrally manage, apply, and verify configuration settings. |
Implementation Point(s): Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, Audit Service wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The Change Management Service supports the ability to provision and audit component configurations on wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The Change Management Service supports the ability to periodically audit component configurations and to compare these audited configurations against approved configurations. The File Integrity Service supports the functionality to verify configuration settings in files on components that support the installation of a File Integrity Service agent. The Change Management Service and File Integrity Service can report any detected unauthorized changes to the appropriate individual either directly (e.g., email notification) or indirectly by sending reports to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| CM-6 Configuration Settings | CM-6-2 The organization employs automated mechanisms to respond to unauthorized changes to [Assignment: organization-defined configuration settings]. |
Implementation Point(s): Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations for access to configuration settings are configured within the Authorization Service and enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The access control functionality reports attempts for unauthorized access to the Audit Service. The Change Management Service supports the ability to periodically audit component configurations and to compare these audited configurations against approved configurations in order to detect any unauthorized changes. The File Integrity Service supports the functionality to detect unauthorized modifications to files on components that support the installation of a File Integrity Service agent. Both the Change Management Service and File Integrity Service report any detected unauthorized changes. The Change Management Service and File Integrity Service can report any detected unauthorized changes to the appropriate individual either directly (e.g., email notification) or indirectly by sending reports to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| CM-6 Configuration Settings | CM-6-3 The organization incorporates detection of unauthorized, security-relevant configuration changes into the organization’s incident response capability to ensure that such detected events are tracked, monitored, corrected, and available for historical purposes. |
Implementation Point(s): Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations for access to configuration settings are configured within the Authorization Service and enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The access control functionality reports attempts for unauthorized access to the Audit Service. The Change Management Service supports the ability to periodically audit component configurations and to compare these audited configurations against approved configurations in order to detect any unauthorized changes. The File Integrity Service supports the functionality to detect unauthorized modifications to files on components that support the installation of a File Integrity Service agent. Both the Change Management Service and File Integrity Service report any detected unauthorized changes. The Change Management Service and File Integrity Service can report any detected unauthorized changes to the appropriate individual either directly (e.g., email notification) or indirectly by sending reports to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| CM-7 Least Functionality | CM-7-A The organization configures the information system to provide only essential capabilities and specifically prohibits or restricts the use of the following functions, ports, protocols, and/or services: [Assignment: organization-defined list of prohibited or restricted functions, ports, protocols, and/or services]. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components are configured to provide only essential capabilities and prohibits and/or restricts the use of the following functions, ports, protocols, and/or services: [Assignment: organization-defined list of prohibited and/or restricted functions, ports, protocols, and/or services]. |
S |
| CM-7 Least Functionality | CM-7-2 The organization employs automated mechanisms to prevent program execution in accordance with [Selection (one or more): list of authorized software programs; list of unauthorized software programs; rules authorizing the terms and conditions of software program usage]. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: The wired workstations are configured such that their operating system prevents program execution in accordance with [Selection (one or more): list of authorized software programs; list of unauthorized software programs; rules authorizing the terms and conditions of software program usage]. |
S |
| CM-8 Information System Component Inventory | CM-8-2 The organization employs automated mechanisms to help maintain an up-to-date, complete, accurate, and readily available inventory of information system components. |
Implementation Point(s): Change Management Service Description: The Change Management Service supports the ability to audit component configurations for automated inventory purposes. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented in the black network Change Management Service. |
C |
| CM-8 Information System Component Inventory | CM-8-3 The organization: (a) Employs automated mechanisms [Assignment: organization-defined frequency] to detect the addition of unauthorized components/devices into the information system; and (b) Disables network access by such components/devices or notifies designated organizational officials. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, WIDS Service, sensors, user and perimeter wireless bridges and black wired/wireless components. Description: The only wireless device authorized to connect to the perimeter wireless bridge is the user wireless bridge following successful completion of 802.1X port-based authentication supported by the Authentication and Authorization Service. The WIDS Service together with its sensors monitor and report detected unauthorized wireless components. For black wired/wireless components, the security control requirement is implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service, WIDS Service, black sensors and black user and perimeter wireless bridges. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| CP-9 Information System Backup | CP-9-A The organization conducts backups of user-level information contained in the information system [Assignment: organization-defined frequency consistent with recovery time and recovery point objectives]. |
Implementation Point(s): Backup and Recovery Service and Information Management Service. Description: The Backup and Recovery Service conducts backups of user-level information maintained by the Information Management Service [Assignment: organization-defined frequency consistent with recovery time and recovery point objectives]. |
C |
| CP-9 Information System Backup | CP-9-B The organization conducts backups of system-level information contained in the information system [Assignment: organization-defined frequency consistent with recovery time and recovery point objectives]. |
Implementation Point(s): Backup and Recovery Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The Backup and Recovery Service accesses the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter to back up system-level information [Assignment: organization-defined frequency consistent with recovery time and recovery point objectives]. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Backup and Recovery Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| CP-9 Information System Backup | CP-9-C The organization conducts backups of information system documentation including security-related documentation [Assignment: organization-defined frequency consistent with recovery time and recovery point objectives]. |
Implementation Point(s): Backup and Recovery Service and Information Management Service. Description: The Backup and Recovery Service conducts backups of information system documentation and these backups are maintained by the Information Management Service [Assignment: organization-defined frequency consistent with recovery time and recovery point objectives]. |
C |
| CP-9 Information System Backup | CP-9-6 The organization accomplishes information system backup by maintaining a redundant secondary system, not collocated, that can be activated without loss of information or disruption to the operation. |
Implementation Point(s): All Description: A fully redundant secondary information system is maintained to support continued information system availability in the event of failure to the primary information system. |
S |
| CP-10 Information System Recovery and Reconstitution | CP-10-2 The information system implements transaction recovery for systems that are transaction-based. |
Implementation Point(s): Information Management Service Description: Support for transaction recovery is implemented in the databases maintained within the Information Management Service. |
C |
| CP-10 Information System Recovery and Reconstitution | CP-10-5 The organization provides [Selection: real-time; near-real-time] [Assignment: organization-defined failover capability for the information system]. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter are implemented in a manner that supports [Selection: real-time; near-real-time] [Assignment: organization-defined failover capability for the information system]. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-A The information system uniquely identifies and authenticates organizational users (or processes acting on behalf of organizational users). |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Accounts credentials are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-1 The information system uses multifactor authentication for network access to privileged accounts. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Multifactor authentication is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and enforced within the network access login functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
- |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-2 The information system uses multifactor authentication for network access to non-privileged accounts. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Internal wired users do not log into the authentication gateway through network access connections. |
- |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-3 The information system uses multifactor authentication for local access to privileged accounts. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Multifactor authentication is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-4 The information system uses multifactor authentication for local access to non-privileged accounts. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and wired workstations. Description: Multifactor authentication is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations. |
S |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-5 The organization: (a) Allows the use of group authenticators only when used in conjunction with an individual/unique authenticator; and (b) Requires individuals to be authenticated with an individual authenticator prior to using a group authenticator. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Group authenticator credentials are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and internal wired users. The use of group authenticators is enforced within the login functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter for wireless component administrators. The use of group authenticators is enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations for internal wired users. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components for black wireless component administrators. |
S |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-6 The information system uses multifactor authentication for network access to privileged accounts where one of the factors is provided by a device separate from the information system being accessed. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Multifactor authentication is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and enforced within the network access login functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. One of the factors is provided by a device separate from the information system being accessed. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
- |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-7 The information system uses multifactor authentication for network access to non-privileged accounts where one of the factors is provided by a device separate from the information system being accessed. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Internal wired users do not log into the authentication gateway through network access connections. |
- |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-8 The information system uses [Assignment: organization-defined replay-resistant authentication mechanisms] for network access to privileged accounts. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The authentication method configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and enforced within the network access login functionality of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter, uses [Assignment: organization-defined replay-resistant authentication mechanisms]. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
- |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-9 The information system uses [Assignment: organization-defined replay-resistant authentication mechanisms] for network access to non-privileged accounts. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Internal wired users do not log into the authentication gateway through network access connections. |
- |
| IA-2 Identification and Authentication (Organizational Users) | IA-2-100 The information system uses multifactor authentication for remote access to privileged accounts. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Wireless component administrators do not use remote access connections to administer the wireless components. |
- |
| IA-3 Device Identification and Authentication | IA-3-A The information system uniquely identifies and authenticates [Assignment: organization-defined list of specific and/or types of devices] before establishing a connection. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges Description: The user wireless bridge bi-directionally authenticates itself to the perimeter wireless bridge using cryptography. The authentication is supported by the 802.1X port-based authentication functionality of the Authentication and Authorization Service. |
S |
| IA-3 Device Identification and Authentication | IA-3-1 The information system authenticates devices before establishing remote and wireless network connections using bidirectional authentication between devices that is cryptographically based. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges Description: The user wireless bridge bi-directionally authenticates itself to the perimeter wireless bridge using cryptography. The authentication is supported by the 802.1X port-based authentication functionality of the Authentication and Authorization Service. |
S |
| IA-3 Device Identification and Authentication | IA-3-2 The information system authenticates devices before establishing network connections using bidirectional authentication between devices that is cryptographically based. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges Description: The user wireless bridge bi-directionally authenticates itself to the perimeter wireless bridge using cryptography. The authentication is supported by the 802.1X port-based authentication functionality of the Authentication and Authorization Service. |
S |
| IA-4 Identifier | IA-4-5 The information system dynamically manages identifiers, attributes, and associated access authorizations. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: The use of dynamic management of identifiers, attributes, and associated access authorizations is not applicable to the business use case. |
- |
| IA-5 Authenticator Management | IA-5-1 The information system, for password-based authentication: (a) Enforces minimum password complexity of [Assignment: organization-defined requirements for case sensitivity, number of characters, mix of upper-case letters, lower-case letters, numbers, and special characters, including minimum requirements for each type]; (b) Enforces at least a [Assignment: organization-defined number of changed characters] when new passwords are created; (c) Encrypts passwords in storage and in transmission; (d) Enforces password minimum and maximum lifetime restrictions of [Assignment: organization-defined numbers for lifetime minimum, lifetime maximum]; and (e) Prohibits password reuse for [Assignment: organization-defined number] generations. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Internal wired user accounts and wireless component administrator accounts are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service to enforce (a) minimum password complexity of [Assignment: organization-defined requirements for case sensitivity, number of characters, mix of upper-case letters, lower-case letters, numbers, and special characters, including minimum requirements for each type]; (b) at least a [Assignment: organization-defined number of changed characters] when new passwords are created; (c) encrypts passwords in storage and in transmission; (d) password minimum and maximum lifetime restrictions of [Assignment: organization-defined numbers for lifetime minimum, lifetime maximum]; and (e) prevention of password reuse for [Assignment: organization-defined number] generations. Login using the password policy is supported by the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| IA-5 Authenticator Management | IA-5-2 The information system, for PKI-based authentication: (a) Validates certificates by constructing a certification path with status information to an accepted trust anchor; (b) Enforces authorized access to the corresponding private key; and (c) Maps the authenticated identity to the user account. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, PKI Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: PKI-based authentication is configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and supported by the PKI Service to (a) validate certificates by constructing a certification path with status information to an accepted trust anchor; (b) enforce authorized access to the corresponding private key; and (c) map the authenticated identity to the user account. PKI-based authentication is supported by the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service, PKI Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| IA-6 Authenticator Feedback | IA-6-A The information system obscures feedback of authentication information during the authentication process to protect the information from possible exploitation/use by unauthorized individuals. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter obscures feedback of authentication information during the login process. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| IA-7 Cryptographic Module Authentication | IA-7-A The information system uses mechanisms for authentication to a cryptographic module that meet the requirements of applicable CSEC guidance for such authentication. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authentication methods are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the login functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. The authentication methods meet the requirements of applicable requirements of applicable CSEC guidance for such authentication. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and login functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| IA-8 Identification and Authentication (Non- Organizational Users) | NA | This security control and its technology-related control elements are not applicable to this business use case since it does not support wireless access for non-departmental users. | - |
| MA-4 Non-Local Maintenance | NA | This security control and its technology-related control elements are not applicable to this business use case which does not include support for non-local maintenance and diagnostic activities. | - |
| SC-2 Application Partitioning | SC-2-A The information system separates user functionality (including user interface services) from information system management functionality. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service includes support for a management sub-zone to separate user services from management services. |
C |
| SC-2 Application Partitioning | SC-2-1 The information system prevents the presentation of information system management-related functionality at an interface for general (i.e., non-privileged) users. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service includes support for a management sub-zone and internal wired user zone to separate system management-related functionality from non-privileged (i.e., external user) functionality. |
C |
| SC-3 Security Function Isolation | SC-3-A The information system isolates security functions from non-security functions. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-3 Security Function Isolation | SC-3-1 The information system implements underlying hardware separation mechanisms to facilitate security function isolation. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter and the black wired/wireless components. Description: Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter each employs underlying hardware separation mechanisms to facilitate security function isolation. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-3 Security Function Isolation | SC-3-2 The information system isolates security functions enforcing access and information flow control from both non-security functions and from other security functions. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and internal wired user perimeter. Description: Access and information flow control security functions are implemented within the Authentication and Authorization Service and Internal wired user perimeter which are separate from the non-security functions performed in the information system. |
S |
| SC-3 Security Function Isolation | SC-3-3 The organization implements an information system isolation boundary to minimize the number of non-security functions included within the boundary containing security functions. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter each minimizes the number of non-security functions included within the isolation boundary containing security functions. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-3 Security Function Isolation | SC-3-4 The organization implements security functions as largely independent modules that avoid unnecessary interactions between modules. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter each implement security functions as largely independent modules that avoid unnecessary interactions between modules. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-3 Security Function Isolation | SC-3-5 The organization implements security functions as a layered structure minimizing interactions between layers of the design and avoiding any dependence by lower layers on the functionality or correctness of higher layers. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter each implement security functions as a layered structure minimizing interactions between layers of the design and avoiding any dependence by lower layers on the functionality or correctness of higher layers. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-4 Information in shared Resources | SC-4-A The information system prevents unauthorized and unintended information transfer via shared system resources. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators that define what information the users and administrators are authorized to access. These authorizations are enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter and are designed to prevent unauthorized and unintended information transfer via shared system resources. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-4 Information in shared Resources | SC-4-1 The information system does not share resources that are used to interface with systems operating at different security levels. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: The interfacing of information systems with different security levels is not applicable to the business use case. |
- |
| SC-5 Denial of Service Protection | SC-5-A The information system protects against or limits the effects of the following types of denial of service attacks: [Assignment: organization-defined list of types of denial of service attacks or reference to source for current list]. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors, and IDS Service. Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors monitor for denial of service attacks within the internal wired user zone while the IDS Service monitors for denial of service attacks within the rest of the departmental network. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SC-5 Denial of Service Protection | SC-5-1 The information system restricts the ability of users to launch denial of service attacks against other information systems or networks. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors, and IDS Service. Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors monitor for denial of service attacks within the internal wired user zone while the IDS Service monitors for denial of service attacks within the rest of the departmental network. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SC-5 Denial of Service Protection | SC-5-2 The information system manages excess capacity, bandwidth, or other redundancy to limit the effects of information flooding types of denial of service attacks. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service’s routers support the assignment of traffic volume thresholds for network traffic types to limit the effects of information flooding types of denial of service attacks. |
C |
| SC-6 Resource Priority | SC-6-A The information system limits the use of resources by priority. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service’s routers support the assignment of traffic volume thresholds for network traffic types to limit use of resources by priority through traffic types. |
C |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-A The information system monitors and controls communications at the external boundary of the system and at key internal boundaries within the system. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The perimeters used to implement departmental network zones (including the internal wired user perimeter) monitors and controls communications at the internal wired user zone boundary to the departmental network. Security of communications with external networks is not within the scope of the business use case. |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-B The information system connects to external networks or information systems only through managed interfaces consisting of boundary protection devices arranged in accordance with a organizational security architecture. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Security of communications with external networks is not within the scope of the business use case. |
- |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-1 The organization physically allocates publicly accessible information system components to separate sub-networks with separate physical network interfaces. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Security of publicly accessible information system components is not within the scope of the business use case. |
- |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-2 The information system prevents public access into the organization’s internal networks except as appropriately mediated by managed interfaces employing boundary protection devices. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Security of public access to the departmental network is not within the scope of the business use case. |
- |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-3 The organization limits the number of access points to the information system to allow for more comprehensive monitoring of inbound and outbound communications and network traffic. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: Access points to the departmental network for internal wired users are limited to the internal wired user perimeter. |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-4 The organization: (a) Implements a managed interface for each external telecommunication service; (b) Establishes a traffic flow policy for each managed interface; (c) Employs security controls as needed to protect the confidentiality and integrity of the information being transmitted; (d) Documents each exception to the traffic flow policy with a supporting mission/business need and duration of that need; (e) Reviews exceptions to the traffic flow policy [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]; and (f) Removes traffic flow policy exceptions that are no longer supported by an explicit mission/business need. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Security of communications with external networks is not within the scope of the business use case. |
- |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-5 The information system at managed interfaces, denies network traffic by default and allows network traffic by exception (i.e., deny all, permit by exception). |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter is configured to deny network traffic by default and allow network traffic by exception (i.e., deny all, permit by exception). |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-6 The organization prevents the unauthorized release of information outside of the information system boundary or any unauthorized communication through the information system boundary when there is an operational failure of the boundary protection mechanisms. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter fails in the open state to prevent the unauthorized release of information outside of the information system boundary or any unauthorized communication through the information system boundary when there is an operational failure of the perimeter. |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-7 The information system prevents remote devices that have established a non-remote connection with the system from communicating outside of that communications path with resources in external networks. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Use of remote devices is not applicable to the business use case. |
- |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-8 The information system routes [Assignment: organization-defined internal communications traffic] to [Assignment: organization-defined external networks] through authenticated proxy servers within the managed interfaces of boundary protection devices. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Security of communications with external networks is not within the scope of the business use case. |
- |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-9 The information system, at managed interfaces, denies network traffic and audits internal users (or malicious code) posing a threat to external information systems. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service and Audit Service. Description: The Network Service perimeters used to implement departmental network zones (including the external user and external administrator gateway components) denies unauthorized communications and sends audit records of these communications (associated with internal users (or malicious code) posing a threat to external information systems) to the Audit Service. |
C |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-10 The organization prevents the unauthorized exfiltration of information across managed interfaces. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The perimeters used to implement departmental network zones (including the Internal wired user perimeter) prevent the unauthorized exfiltration of information. |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-11 The information system checks incoming communications to ensure that the communications are coming from an authorized source and routed to an authorized destination. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The perimeters used to implement departmental network zones (including the Internal wired user perimeter) check incoming communications to ensure that the communications are coming from an authorized source and routed to an authorized destination. |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-12 The information system implements host-based boundary protection mechanisms for servers, workstations, and mobile devices. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Host-based boundary protection mechanisms are implemented on the User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented on the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-13 The organization isolates [Assignment: organization defined key information security tools, mechanisms, and support components] from other internal information system components via physically separate subnets with managed interfaces to other portions of the system. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service implements zones and sub-zones used to segregate components within the departmental network based on their security policies. |
C |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-15 The information system routes all networked, privileged accesses through a dedicated, managed interface for purposes of access control and auditing. |
Implementation Point(s): Perimeter wired switches, perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The perimeter wired switches, perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter each support a separate management network interface that connects to the management sub-zone. The management network interfaces are used for wireless component administrator access to the components and support administrative access control and auditing. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the security control requirement is also implemented on the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-16 The information system prevents discovery of specific system components (or devices) composing a managed interface. |
Implementation Point(s): Perimeter wired switches, perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The perimeter wired switches, perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components each support a separate management network interface that connects to the management sub-zone. These management network interfaces do not respond to network discovery tools or techniques. |
S |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-17 The organization employs automated mechanisms to enforce strict adherence to protocol format. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service implements zones and sub-zones used to segregate components within the departmental network based on their security policies. The perimeter components that separate zones and sub-zones enforce strict adherence to protocol format and deny communications that don’t comply. |
C |
| SC-7 Boundary Protection | SC-7-18 The information system fails securely in the event of an operational failure of a boundary protection device. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service implements zones and sub-zones used to segregate components within the departmental network based on their security policies. The perimeter components that separate zones and sub-zones fail in a secure manner by denying all communication in their failed state. |
C |
| SC-8 Transmission Integrity | SC-8-A The information system protects the integrity of transmitted information. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption is supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is also Type 1 encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. |
S |
| SC-8 Transmission Integrity | SC-8-1 The organization employs cryptographic mechanisms to recognize changes to information during transmission unless otherwise protected by alternative physical measures. The cryptography must be compliant with the requirements of control SC-13. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: AES encryption is supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is also Type 1 encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. The cryptography used in both cases is compliant with the requirements of control SC-13. |
S |
| SC-8 Transmission Integrity | SC-8-2 The information system maintains the integrity of information during aggregation, packaging, and transformation in preparation for transmission. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: AES encryption is supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is also Type 1 encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. |
S |
| SC-9 Transmission Confidentiality | SC-9-A The information system protects the confidentiality of transmitted information. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: AES encryption is supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is also Type 1 encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. |
S |
| SC-9 Transmission Confidentiality | SC-9-1 The organization employs cryptographic mechanisms to prevent unauthorized disclosure of information during transmission unless otherwise protected by [Assignement: organization-defined alternative physical measures]. The cryptography must be compliant with the requirements of control SC-13. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: AES encryption is supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is also Type 1 encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. The cryptography used in both cases is compliant with the requirements of control SC-13. |
S |
| SC-9 Transmission Confidentiality | SC-9-2 The information system maintains the confidentiality of information during aggregation, packaging, and transformation in preparation for transmission. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: AES encryption is supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is also Type 1 encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. The user and perimeter wireless bridges and user and perimeter INEs maintain the confidentiality of information during aggregation, packaging, and transformation in preparation for transmission. |
S |
| SC-9 Transmission Confidentiality | SC-9-100 The organization employs traffic flow security to protect communications against traffic flow analysis. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter INEs. Description: For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments, traffic flow security mechanisms are implemented within the user and perimeter INEs to protect communications against traffic flow analysis. |
S |
| SC-10 Network Disconnect | SC-10-A The information system terminates the network connection associated with a communications session at the end of the session or after [Assignment: organization-defined time period] of inactivity. |
Implementation Point(s): Internal wired user perimeter Description: The internal wired user perimeter is configured to terminate network connections at the end of a session or after [Assignment: organization-defined time period] of inactivity. |
S |
| SC-11 Trusted Path | SC-11-A The information system establishes a trusted communications path between the user and the following security functions of the system: [Assignment: organization-defined security functions to include at a minimum, information system authentication and re-authentication]. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, perimeter wired switches, perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Wireless component administrators access the perimeter wired switches, perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter using their administrator workstations located within the management sub-zone implemented by the Network Service. The information flow policies enforced within the restricted zone and operations zone ensure that administration of the wireless components can only be performed from internal administrator workstations located in the management sub-zone. The path between the internal administrators and the wireless components is therefore trusted. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented for black wired/wireless components using a black management sub-zone. |
S |
| SC-12 Cryptographic Key Establishment and Management | SC-12-A The organization establishes and manages cryptographic keys for required cryptography employed within the information system. |
Implementation Point(s): PKI Service Description: The PKI Service establishes and manages cryptographic keys for required cryptography employed within the information system. |
C |
| SC-12 Cryptographic Key Establishment and Management | SC-12-2 The organization produces, controls, and distributes symmetric cryptographic keys using CSEC-approved key managementFootnote 3 technology and processes. |
Implementation Point(s): PKI Service Description: The PKI Service produces, controls, and distributes symmetric cryptographic keys using CSEC-approved key management technology and processes in accordance with CSEC-approved key management technology and processes. |
C |
| SC-12 Cryptographic Key Establishment and Management | SC-12-3 The organization produces, controls, and distributes symmetric and asymmetric cryptographic keys using CSEC-approved key management technology and processes. |
Implementation Point(s): PKI Service Description: The PKI Service produces, controls, and distributes symmetric and asymmetric cryptographic keys using CSEC-approved key management technology and processes. |
C |
| SC-12 Cryptographic Key Establishment and Management | SC-12-4 The organization produces, controls, and distributes asymmetric cryptographic keys using approved PKI Class 3Footnote 4 certificates or prepositioned keying material. |
Implementation Point(s): PKI Service Description: The PKI Service produces, controls, and distributes asymmetric cryptographic keys using approved PKI Class 3 certificates or prepositioned keying material. |
C |
| SC-12 Cryptographic Key Establishment and Management | SC-12-5 The organization produces controls, and distributes asymmetric cryptographic keys using approved PKI Class 3 or Class 4 certificates and hardware security tokens that protect the user’s private key. |
Implementation Point(s): PKI Service Description: The PKI Service produces controls, and distributes asymmetric cryptographic keys using approved PKI Class 3 or Class 4 certificates and hardware security tokens that protect the user’s private key. |
C |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-A The information system implements cryptographic protections using cryptographic systems that comply with applicable GC legislation and TBS policies, directives and standards. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: AES encryption is supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is also Type 1 encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. Encryption is implemented using cryptographic systems that comply with applicable GC legislation and TBS policies, directives and standards. |
S |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-1 The organization employs, at a minimum, CMVP-validated cryptography to protect Unclassified data. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges. Description: AES encryption is supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. Encryption is implemented using CMVP-validated cryptography to protect Unclassified data. |
S |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-2 The organization employs CSEC-approved cryptography to protect Classified data. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter INEs. Description: For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter INEs. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. Encryption is implemented using CSEC approved cryptography to protect Classified data. |
S |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-3 The organization employs, at a minimum, CMVP-validated cryptography to protect data when such data must be separated from individuals who have the necessary clearances yet lack the necessary access approvals. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter use CMVP-validated cryptography (at a minimum) to protect information when such information must be separated from individuals who have the necessary clearances yet lack the necessary access approvals. |
S |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-4 The organization employs [Selection: CMVP-validated; CSEC-approved] cryptography to implement digital signatures. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: Encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is also encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wired user zone. [Selection: CMVP-validated; CSEC-approved] cryptography is used by these components to implement digital signatures for the encrypted communications. |
S |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-100 The organization employs CMVP-validated cryptography to protect Protected A data in transmission. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges. Description: Encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges for Protected A data in transmission. Encryption is implemented using CMVP-validated cryptography to protect the Protected A data in transmission. |
S |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-101 The organization employs CMVP-validated cryptography to protect Protected B data in transmission. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges. Description: Encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges for Protected B data in transmission. Encryption is implemented using CMVP-validated cryptography to protect the Protected B data in transmission. |
S |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-102 The organization employs CSEC-approved cryptography to protect Protected C data in transmission. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter INEs. Description: For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter INEs. The encryption protects the integrity and confidentiality of the information transmitted in the internal wireless user zone. Encryption is implemented using CSEC-approved cryptography to protect Protected C data in transmission. |
S |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-103 The organization employs [Selection: CMVP-validated; CSEC-approved] cryptography to protect Protected [selection: organizationally-defined data] at rest. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: The wired workstations are configured with cryptographic mechanisms to protect the confidentiality and integrity of their Protected information at rest. The [Selection: CMVP-validated; CSEC-approved] cryptography is used to protect Protected [selection: organizationally-defined data] at rest. |
- |
| SC-13 Use of Cryptography | SC-13-104 The organization uses COMSEC equipment in accordance with CSEC ITSD-01 Directives for the Application of Communications Security in the Government of Canada. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter INEs. Description: The user and perimeter INEs are used in accordance with CSEC ITSD-01 Directives for the Application of Communications Security in the Government of Canada. |
S |
| SC-14 Public Access Protections | NA | This security control and its technology-related control elements are not applicable to this business use case as it does not involve the protection of integrity and availability of publicly available information and applications | - |
| SC-16 Transmission of Security Attributes | NA | This security control and its technology-related control elements are not applicable to this business use case as it does not involve the exchange of information and their associated security attributes between separate information systems (i.e., the departmental network and some other information system) is not applicable the business use case. | - |
| SC-18 Mobile Code | SC-18-C The organization authorizes, monitors, and controls the use of mobile code within the information system. |
Implementation Point(s): MCDS and wired workstations. Description: The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data for mobile code and to take the appropriate action. |
S |
| SC-18 Mobile Code | SC-18-1 The information system implements detection and inspection mechanisms to identify unauthorized mobile code and takes corrective actions, when necessary. |
Implementation Point(s): Malicious Code Defence Service, wired workstations and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data for mobile code and to take the appropriate action. The internal wired user perimeter monitors communications leaving and entering the internal wired user zone to detect and inspect data for unauthorized mobile code and to take the appropriate action. |
S |
| SC-18 Mobile Code | SC-18-3 The information system prevents the download and execution of prohibited mobile code. |
Implementation Point(s): MCDS and wired workstations. Description: The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data for unauthorized mobile code and to take the appropriate action. |
S |
| SC-18 Mobile Code | SC-18-4 The information system prevents the automatic execution of mobile code in [Assignment: organization-defined software applications] and requires [Assignment: organization-defined actions] prior to executing the code. |
Implementation Point(s): MCDS and wired workstations. Description: The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data for unauthorized mobile code and to take the appropriate action. |
S |
| SC-20 Secure Name/Address Resolution Service (Authoritative Source) | SC-20-A The information system provides additional data origin and integrity artefacts along with the authoritative data the system returns in response to name/address resolution queries. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The DNS functionality of the Network Service provides name/address resolution service provides additional data origin and integrity artefacts along with the authoritative data it returns in response to resolution queries. |
C |
| SC-20 Secure Name/Address Resolution Service (Authoritative Source) | SC-20-1 The information system, when operating as part of a distributed, hierarchical namespace, provides the means to indicate the security status of child subspaces and (if the child supports secure resolution services) enable verification of a chain of trust among parent and child domains. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The DNS functionality of the Network Service provides the means to indicate the security status of child subspaces and (if the child supports secure resolution services) enable verification of a chain of trust among parent and child domains when operating as part of a distributed, hierarchical namespace. |
C |
| SC-21 Secure Name/Address Resolution Service (Recursive or Caching Resolver) | SC-21-A The information system performs data origin authentication and data integrity verification on the name/address resolution responses the system receives from authoritative sources when requested by client systems. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The DNS functionality of the Network Service performs data origin authentication and data integrity verification only when requested by an internal wired user station. |
C |
| SC-21 Secure Name/Address Resolution Service (Recursive or Caching Resolver) | SC-21-1 The information system performs data origin authentication and data integrity verification on all resolution responses whether or not local clients explicitly request this service. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The DNS functionality of the Network Service always performs data origin authentication and data integrity verification. |
C |
| SC-22 Architecture and Provisioning for Name/Address Resolution Service | SC-22-A The information systems that collectively provide name/address resolution service for a organization are fault-tolerant and implement internal/external role separation. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The DNS functionality of the Network Service is fault tolerant and implements role separation. |
C |
| SC-23 Session Authenticity | SC-23-A The information system provides mechanisms to protect the authenticity of communications sessions. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wireless bridges, user and perimeter INEs. Description: Encrypted communications are supported between the user and perimeter wireless bridges. The encryption protects the authenticity of communications sessions in the internal wired user zone. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the transmitted information is encrypted by the user and perimeter INEs. Encryption is implemented using CSEC-approved encryption mechanisms commensurate for the classification and sensitivity of the information and in accordance with the ITSA-11D CSEC Approved Cryptographic Algorithms for the Protection of Protected Information and for Electronic Authentication and Authorization Applications within the Government of Canada. |
S |
| SC-23 Session Authenticity | SC-23-1 The information system invalidates session identifiers upon user logout or other session termination. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter each invalidate session identifiers upon user logout or other session termination. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-23 Session Authenticity | SC-23-2 The information system provides a readily observable logout capability whenever authentication is used to gain access to web pages. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: If any of the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter requires the use of authentication through a web page, the web page will provide a readily observable logout capability. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-23 Session Authenticity | SC-23-3 The information system generates a unique session identifier for each session and recognizes only session identifiers that are system-generated. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter each use unique session identifiers for each session and recognize only session identifiers that are system-generated. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-23 Session Authenticity | SC-23-4 The information system generates unique session identifiers with [Assignment: organization-defined randomness requirements]. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter each generates unique session identifiers with [Assignment: organization-defined randomness requirements]. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-24 Fail in Known State | SC-24-A The information system fails to a [Assignment: organization-defined known-state] for [Assignment: organization-defined types of failures] preserving [Assignment: organization-defined system state information] in failure. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, access points user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter fail to a [Assignment: organization-defined known-state] for [Assignment: organization-defined types of failures]. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-25 Thin Nodes | NA | This security control and its technology-related control elements are not applicable to this business use case since it does not include the use of thin nodes. | - |
| SC-26 Honeypots | NA | This security control and its technology-related control elements are not applicable to this business use case since it does not include the use of honey pots. | - |
| SC-27 Operating System-Independent Applications | SC-27-A The information system includes: [Assignment: organization-defined operating system- independent applications]. |
Implementation Point(s): NA Description: Security of applications accessed by the internal wired users is not within scope of the business use case. |
S |
| SC-28 Protection of Information at Rest | SC-28-A The information system protects the confidentiality and integrity of information at rest. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: The wired workstations are configured to protect the confidentiality of their information at rest. |
S |
| SC-28 Protection of Information at Rest | SC-28-1 The organization employs cryptographic mechanisms to prevent unauthorized disclosure and modification of information at rest unless otherwise protected by alternative physical measures. The cryptography is compliant with the requirements of control SC-13. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: The wired workstations are configured with cryptographic mechanisms to protect the confidentiality and integrity of their information at rest. The cryptography is compliant with the requirements of control SC-13. |
S |
| SC-29 Heterogeneity | SC-29-A The organization employs diverse information technologies in the implementation of the information system. |
Implementation Point(s): Access points, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The use of diverse information technologies is supported within the access points user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. However this may not be possible if the wireless components are selected from a single vendor to facilitate successful integration with each other. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-30 Virtualization Techniques | SC-30-A The organization employs virtualization techniques to present information system components as other types of components, or components with differing configurations. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The use of virtualization techniques is supported within the user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. However this may not be possible if the wireless components are firmware-based appliances rather than operating system-based components. Firmware-based appliances are typically less flexible than operating system-based components in their configuration and therefore it may not allow for the possibility to configure the appliances as other types of components. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-30 Virtualization Techniques | SC-30-1 The organization employs virtualization techniques to support the deployment of a diversity of operating systems and applications that are changed [Assignment: organization-defined frequency]. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The use of virtualization techniques is supported within the user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. However this may not be possible if the wireless components are firmware-based appliances rather than operating system-based components. Firmware-based appliances are typically less flexible than operating system-based components in their configuration and therefore it may not allow for the possibility to configure the appliances as other types of components. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-30 Virtualization Techniques | SC-30-2 The organization employs randomness in the implementation of the virtualization techniques. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter use randomness in the implementation of virtualization techniques to present information system components as other types of components. However this may not be possible if the wireless components are firmware-based appliances rather than operating system-based components. Firmware-based appliances are typically less flexible than operating system-based components in their configuration and therefore it may not allow for the possibility to configure the appliances as other types of components. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-32 Information System Partitioning | SC-32-A The organization partitions the information system into components residing in separate physical domains (or environments) as deemed necessary. |
Implementation Point(s): Network Service Description: The Network Service implements zones and sub-zones used to segregate components within the departmental network based on their security policies. |
C |
| SC-33 Transmission Preparation Integrity | SC-33-A The information system protects the integrity of information during the processes of data aggregation, packaging, and transformation in preparation for transmission. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter protect the integrity of information during the processes of data aggregation, packaging, and transformation in preparation for transmission. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-34 Non-Modifiable Executable Programs | SC-34-A The information system at [Assignment: organization-defined information system components] loads and executes the operating environment from hardware-enforced, read-only media. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter identified in [Assignment: organization-defined information system components] load and execute their operating environment from hardware-enforced, read-only media. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SC-34 Non-Modifiable Executable Programs | SC-34-B The information system at [Assignment: organization-defined information system components] loads and executes [Assignment: organization-defined applications] from hardware-enforced, read-only media. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter identified in [Assignment: organization-defined information system components] load and execute [Assignment: organization-defined applications] from hardware-enforced, read-only media. |
S |
| SC-34 Non-Modifiable Executable Programs | SC-34-1 The organization employs [Assignment: organization-defined information system components] with no writeable storage that is persistent across component restart or power on/off. |
Implementation Point(s): User and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter identified in [Assignment: organization-defined information system components] are configured with no writeable storage that is persistent across component restart or power on/off. |
S |
| SC-100 Source Authentication | SC-100-A The information system allows a message recipient to verify the claimed source identifier in a message. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Functionality for verification of claimed source identifier in a message is supported within the operating system and applications hosted on the wired workstations. |
- |
| SC-100 Source Authentication | SC-100-1 Authentication of the claimed identifier in the message is cryptographically based. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Functionality for verification of claimed source identifier in a message i supported within the operating system and applications hosted on the wired workstations and is cryptographically based. |
- |
| SC-100 Source Authentication | SC-100-2 The organization employs CMVP-certified cryptography for digital signature generation and verification. Refer to control SC-13. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Functionality for verification of claimed source identifier in a message is supported within the operating system and applications hosted on the wired workstations and employs CMVP-certified cryptography for digital signature generation and verification. |
- |
| SC-100 Source Authentication | SC-100-3 The organization employs CSEC-approved cryptography and protocols to implement the authentication. Refer to control SC-13. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations Description: Functionality for verification of claimed source identifier in a message is supported within the operating system and applications hosted on the wired workstations and employs CSEC-approved cryptography and protocols to implement the authentication. |
- |
| SC-101 Unclassified Telecommunications Systems in Secure Facilities | NA | This security control and its technology-related control elements are not applicable to this business use case since it does not include the use of Unclassified telecommunications systems in secure facilities. | - |
| SI-2 Flaw Remediation | SI-2-1 The organization centrally manages the flaw remediation process and installs software updates automatically. |
Implementation Point(s): Remediation Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The Remediation Service automates the collection, analysis, and provisioning of software patches to the wired workstations, access points, sensors, perimeter wireless/wired switch, internal wired user perimeter that are compatible with the Remediation Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the Remediation Service is supported on the black network for the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-2 Flaw Remediation | SI-2-2 The organization employs automated mechanisms [Assignment: organization-defined frequency] to determine the state of information system components with regard to flaw remediation. |
Implementation Point(s): Remediation Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The Remediation Service automates the analysis at [Assignment: organization-defined frequency] of the state of information system components with regard to flaw remediation. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black network Remediation Service for black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-2 Flaw Remediation | SI-2-4 The organization employs automated patch management tools to facilitate flaw remediation to [Assignment: organization-defined information system components]. |
Implementation Point(s): Remediation Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The Remediation Service automates the collection, analysis, and provisioning of software patches to the wired workstations, access points, sensors, perimeter wireless/wired switch, internal wired user perimeter that are compatible with the Remediation Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the Remediation Service is supported on the black network for the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-3 Malicious Code Protection | SI-3-A The organization employs malicious code protection mechanisms at information system entry and exit points and at workstations, servers, or mobile computing devices on the network to detect and eradicate malicious code: (a) transported by electronic mail, electronic mail attachments, web accesses, removable media, or other common means; or (b) inserted through the exploitation of information system vulnerabilities. |
Implementation Point(s): Malicious Code Defence Service, wired workstations and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data to detect and eradicate malicious code. The internal wired user perimeter monitors communications leaving and entering the internal wired user zone to detect and inspect data to detect and eradicate malicious code. |
S |
| SI-3 Malicious Code Protection | SI-3-C The organization configures malicious code protection mechanisms to: (a) perform periodic scans of the information system [Assignment: organization-defined frequency] and real-time scans of files from external sources as the files are downloaded, opened, or executed in accordance with organizational security policy; and (b) [Selection (one or more): block malicious code; quarantine malicious code; send alert to administrator; [Assignment: organization-defined action]] in response to malicious code detection. |
Implementation Point(s): Malicious Code Defence Service, wired workstations and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to include periodic scans [Assignment: organization-defined frequency] and real-time scans of files from external sources as the files are downloaded, opened, or executed in accordance with organizational security policy; and [Selection (one or more): block malicious code; quarantine malicious code; send alert to administrator; [Assignment: organization-defined action]] in response to malicious code detection. |
S |
| SI-3 Malicious Code Protection | SI-3-1 The organization centrally manages malicious code protection mechanisms. |
Implementation Point(s): Malicious Code Defence Service, wired workstations and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The MCDS centrally manages malicious code protection mechanisms implemented on the wired workstations and internal wired user perimeter. |
S |
| SI-3 Malicious Code Protection | SI-3-2 The information system automatically updates malicious code protection mechanisms (including signature definitions). |
Implementation Point(s): Malicious Code Defence Service Description: The MCDS includes the ability to automatically update its supporting software components or signature definitions. |
C |
| SI-3 Malicious Code Protection | SI-3-3 The information system prevents non-privileged users from circumventing malicious code protection capabilities. |
Implementation Point(s): Malicious Code Defence Service, Authentication and Authorization Service and wired workstations. Description: The wired workstations are configured with malicious code defence agents that operate under the policies defined within the MCDS to detect and inspect data to detect and eradicate malicious code. Authorizations to the agents’ configuration are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and are enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations to prevent circumvention of host-based malicious code protection capabilities. |
S |
| SI-3 Malicious Code Protection | SI-3-4 The information system updates malicious code protection mechanisms only when directed by a privileged user. |
Implementation Point(s): Malicious Code Defence Service Description: The MCDS includes the ability to automatically update its supporting software components or signature definitions when directed by appropriately privileged administrator. |
C |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-A The organization monitors events on the information system in accordance with [Assignment: organization-defined monitoring objectives] and detects information system attacks. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors, and IDS Service Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors monitor for events on the information system in accordance with [Assignment: organization-defined monitoring objectives] and detects information system attacks within the internal wired user zone while the IDS Service monitors for denial of service attacks within the rest of the departmental network. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-C The organization deploys monitoring devices: (a) strategically within the information system to collect organization-determined essential information; and (b) at ad hoc locations within the system to track specific types of transactions of interest to the organization. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors, and IDS Service Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors are deployed (i) strategically within the internal wired user zone to collect organization-determined essential information; and (ii) at ad hoc locations within the system to track specific types of transactions of interest to the organization. The IDS Service monitors for denial of service attacks within the rest of the departmental network. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-1 The organization interconnects and configures individual intrusion detection tools into a system wide intrusion detection system using common protocols. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and IDS Service Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors integrates with the IDS Service to provide a system wide intrusion detection system. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors and cannot integrate with the IDS Service. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-2 The organization employs automated tools to support near real-time analysis of events. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and IDS Service Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors support near-real-time analysis of events within the internal wired user zone while the IDS Service supports near-real-time analysis of events within the rest of the departmental network. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-3 The organization employs automated tools to integrate intrusion detection tools into access control and flow control mechanisms for rapid response to attacks by enabling reconfiguration of these mechanisms in support of attack isolation and elimination. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors integrates with the internal wired user perimeter to control information flow in order to support attack isolation and elimination. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors and cannot integrate with the internal wired user perimeter. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-4 The information system monitors inbound and outbound communications for unusual or unauthorized activities or conditions. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors and the internal wired user perimeter monitor inbound and outbound communications for unusual or unauthorized activities or conditions. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-5 The information system provides near real-time alerts when the following indications of compromise or potential compromise occur: [Assignment: organization-defined list of compromise indicators]. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and IDS Service. Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors detects events within the internal wired user zone and provides a real-time alert when the following indications of compromise or potential compromise occur: [Assignment: organization-defined list of compromise indicators]. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-6 The information system prevents non-privileged users from circumventing intrusion detection and prevention capabilities. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service and wired workstations. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations to prevent internal wired users from circumventing host-based intrusion detection and prevention capabilities. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-7 The information system notifies [Assignment: organization-defined list of incident response personnel (identified by name and/or by role)] of suspicious events and takes [Assignment: organization-defined list of least-disruptive actions to terminate suspicious events]. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, IDS Service and Audit Service. Description: The WIDS Service, IDS Service and Audit Service notify [Assignment: organization-defined list of incident response personnel] of suspicious events and takes [Assignment: organization-defined list of least-disruptive actions to terminate suspicious events]. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the WIDS Service and Audit Service are implemented within the black network. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-8 The organization protects information obtained from intrusion-monitoring tools from unauthorized access, modification, and deletion. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for wireless component administrators and enforced within the access control functionality of the WIDS and IDS Services. These authorizations ensure that information obtained from intrusion monitoring tools shall be protected against unauthorized access, modification, and deletion. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments, the authorizations are assigned within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service for black wireless component administrators and enforced within the access control functionality of the black WIDS Service. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-10 The organization makes provisions so that encrypted traffic is visible to information system monitoring tools. |
Implementation Point(s): IDS Service Description: Internal wired user content can be viewed, listened to, or captured in real-time provided it is not encrypted. The internal wired user communications between the user and perimeter wireless bridges are encrypted. The IDS Service can be used to access the unencrypted content at the internal wired user perimeter. |
C |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-11 The organization analyzes outbound communications traffic at the external boundary of the system (i.e., system perimeter) and, as deemed necessary, at selected interior points within the system (e.g., subnets, subsystems) to discover anomalies. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The WIDS Service together with its sensors and the internal wired user perimeter monitor inbound and outbound communications for unusual or unauthorized activities or conditions. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments the WIDS Service is implemented within the black network using black sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-12 The organization employs automated mechanisms to alert security personnel of the following inappropriate or unusual activities with security implications: [Assignment: organization-defined list of inappropriate or unusual activities that trigger alerts]. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors, IDS Service and internal wired user perimeter. Description: The WIDS service together with its sensors, IDS Service and internal wired user perimeter alert security personnel of the following inappropriate or unusual activities with security implications: [Assignment: organization-defined list of inappropriate or unusual activities that trigger alerts]. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-13 The organization: (a) Analyzes communications traffic/event patterns for the information system; (b) Develops profiles representing common traffic patterns and/or events; and (c) Uses the traffic/event profiles in tuning system-monitoring devices to reduce the number of false positives to [Assignment: organization-defined measure of false positives] and the number of false negatives to [Assignment: organization-defined measure of false negatives]. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and IDS Service. Description: The WIDS service together with its sensors and IDS Service (a) analyzes communications traffic/event patterns for the information system; (b) develops profiles representing common traffic patterns and/or events; and (c) uses the traffic/event profiles in tuning system-monitoring devices to reduce the number of false positives to [Assignment: organization-defined measure of false positives] and the number of false negatives to [Assignment: organization-defined measure of false negatives]. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-14 The organization employs a wireless intrusion detection system to identify rogue wireless devices and to detect attack attempts and potential compromises/breaches to the information system. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and IDS Service. Description: The WIDS service together with its sensors monitor wireless communications to identify rogue wireless devices and to detect attack attempts and potential compromises/breaches to the information system. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-4 Information System Monitoring | SI-4-15 The organization employs an intrusion detection system to monitor wireless communications traffic as the traffic passes from wireless to wireline networks. |
Implementation Point(s): WIDS Service, sensors and IDS Service. Description: The WIDS service together with its sensors monitor wireless communications traffic as the traffic passes from wireless to wireline networks. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments the security control requirement is implemented within the black network WIDS Service and sensors. |
S |
| SI-6 Security Functionality Verification | SI-6-A The information system verifies the correct operation of security functions [Selection (one or more): [Assignment: organization-defined system transitional states]; upon command by user with appropriate privilege; periodically every [Assignment: organization-defined time-period] and [Selection (one or more): notifies system administrator; shuts the system down; restarts the system; [Assignment: organization-defined alternative action(s)]] when anomalies are discovered. |
Implementation Point(s): Wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter verify the correct operation of security functions [Selection (one or more): [Assignment: organization-defined system transitional states]; upon command by user with appropriate privilege; periodically every [Assignment: organization-defined time-period] and [Selection (one or more): notifies system administrator; shuts the system down; restarts the system; [Assignment: organization-defined alternative action(s)]] when anomalies are discovered. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-6 Security Functionality Verification | SI-6-1 The information system provides notification of failed automated security tests. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter transmit audit records identifying failed automated security tests to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments this security control requirement is implemented within the black network Audit Service and black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-6 Security Functionality Verification | SI-6-2 The information system provides automated support for the management of distributed security testing. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The access points, sensors, perimeter wireless/wired switch, internal wired user perimeter verify the correct operation of their critical security functions and report the results of these tests in audit records sent to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments, the security control requirement is implemented within the black network Audit Service, and the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-7 Software and Information Integrity | SI-7-A The information system detects unauthorized changes to software and information. |
Implementation Point(s): Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations for access to software, information and functionality are configured within the Authorization Service and enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. Any actions that are not authorized will be reported by the audit capability of the components to the Audit Service. The Change Management Service supports the ability to periodically audit component software and information configurations and to compare these audited configurations against approved configurations in order to detect any unauthorized changes. The File Integrity Service supports the functionality to detect unauthorized modifications to files on components that support the installation of a File Integrity Service agent. The Change Management Service and File Integrity Service can report any detected unauthorized changes to the appropriate individual either directly (e.g., email notification) or indirectly by sending reports to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments, the security control requirement is supported by the black network Change Management Service, File Integrity Service and Audit Service for the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-7 Software and Information Integrity | SI-7-2 The organization employs automated tools that provide notification to designated individuals upon discovering discrepancies during integrity verification. |
Implementation Point(s): Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The Change Management Service and File Integrity Service can report any detected unauthorized changes to the appropriate individual either directly (e.g., email notification) or indirectly by sending reports to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless service deployments, the security control requirement is supported by the black network Change Management Service and File Integrity Service for the black wired/wireless components |
S |
| SI-7 Software and Information Integrity | SI-7-3 The organization employs centrally managed integrity verification tools. |
Implementation Point(s): Change Management Service, File Integrity Service, Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The Change Management Service supports the ability to periodically audit component software and information configurations and to compare these audited configurations against approved configurations in order to detect any unauthorized changes. The File Integrity Service supports the functionality to detect unauthorized modifications to files on components that support the installation of a File Integrity Service agent. The Change Management Service and File Integrity Service can report any detected unauthorized changes to the appropriate individual either directly (e.g., email notification) or indirectly by sending reports to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments, the security control requirement is also supported by the black network Change Management Service, File Integrity Service and Audit Service for the black wired/wireless components |
S |
| SI-8 Spam Protection | SI-8-A The organization employs spam protection mechanisms at information system entry and exit points and at workstations, servers, or mobile computing devices on the network to detect and take action on unsolicited messages transported by electronic mail, electronic mail attachments, web accesses, or other common means. |
Implementation Point(s): Mail Service Description: SPAM protection mechanisms are implemented within the Mail Service accessed by the wired workstations. |
C |
| SI-8 Spam Protection | SI-8-1 The organization centrally manages spam protection mechanisms. |
Implementation Point(s): Mail Service Description: The Mail Service’s SPAM protection software products and their configuration are centrally managed. |
C |
| SI-8 Spam Protection | SI-8-2 The information system automatically updates spam protection mechanisms (including signature definitions). |
Implementation Point(s): Mail Service Description: The Mail Service’s SPAM protection products include the ability to perform automatic updates including signature definitions. |
C |
| SI-9 Information Input Restrictions | SI-9-A The organization restricts the capability to input information to the information system to authorized personnel. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations (when accessing end user services), user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. These authorizations restrict the capability to input information to the information system to authorized personnel only. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments, the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-10 Information Input Validation | SI-10-A The information system checks the validity of information inputs. |
Implementation Point(s): Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Authorizations are assigned within the Authentication and Authorization Service for internal wired users and wireless component administrators and enforced within the access control functionality of the wired workstations (when accessing internal wired user services), user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter. These authorizations restrict the capability to input information to the information system to authorized personnel only. The information is checked for accuracy, completeness, validity, and authenticity at the component where it is inputted. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments, the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-11 Error Handling | SI-11-A The information system identifies potentially security-relevant error conditions. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter support reporting of error conditions to the Audit Service. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments, the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-11 Error Handling | SI-11-B The information system generates error messages that provide information necessary for corrective actions without revealing [Assignment: organization-defined sensitive or potentially harmful information] in error logs and administrative messages that could be exploited by adversaries. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: The auditing functionality of the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter supports the ability to configure the type of events reported to the Audit Service that do not contain potentially harmful information that could be exploited by adversaries. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments, the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Audit Service and audit functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
| SI-11 Error Handling | SI-11-C The information system reveals error messages only to authorized personnel. |
Implementation Point(s): Audit Service, Authentication and Authorization Service, wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors, internal wired user perimeter and black wired/wireless components. Description: Access authorizations for authorized personnel to audit information and tools within the Audit Service are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service and enforced by the Audit Service. Access authorizations for authorized personnel to audit information within the wired workstations, user and perimeter wired switches, user and perimeter wireless bridges, sensors and internal wired user perimeter are configured within the Authentication and Authorization Service and enforced by the access control functionality of the wireless components. For Protected C and Classified wireless services deployments, the security control requirement is also implemented within the black network Authentication and Authorization Service, Audit Service and access control functionality of the black wired/wireless components. |
S |
3 References
- [Reference 1]
- The IEEE Standards Association (standards.iee.org)
- [Reference 2]
- ITSG-33 IT Security Risk Management: A Lifecycle Approach - Overview; CSEC (Nov 2012)
- [Reference 3]
- ITSG-41 Security Requirements for Wireless Local Area Networks; CSEC (March 2013)
- [Reference 4]
- ITSG-41 Annex 1 - Government Hot Spot High-Level Design Guidance; CSEC (March 2013)
- [Reference 5]
- ITSG-41 Annex 2 - Wireless User to Wired Network Connection High-Level Design Guidance; CSEC (March 2013)
- [Reference 6]
- ITSG-41 Annex 4 – Identification of Control Elements from Security Controls; CSEC (March 2013)
- [Reference 7]
- ITSG-38 Network Security Zoning Design Considerations for Placement of Services within Zones; CSEC (May 2009)
- [Reference 8]
- ITSG-13 Cryptographic Key Ordering Manual; CSEC (MAY 2006).